XRF tool, how it works and its applications in EEE parts
- Posted by Francisco Javier Aparicio Rebollo
- On May 16, 2019
- 0
XRF tool is a non-destructive and quick analytical to determine the chemical elements present in the specimen. In particular, it combines low detection limit (particularly in the case of heavy elements) with quick and easy sample preparation.
- Non-destructive analysis character.
- Bulk chemical analyses of the main elements present in the specimen.
- Bulk chemical analyses of trace elements (in abundances >1 ppm) on the sample.
- Detection of Z > 11 elements.
- Recommended for materials where matrix effects are not relevant.
Improve your design in terms of performance, reliability, cost and delivery using doEEEt
Practical Applications
Nowadays XRF is extensively used to test electronic systems (components, devices, PCB, and final products). These analyses are demanded for different applications such as:
- Compliance verification of RoHS regulations (Restrictions of Hazardous Substances). In this case, the analysis focuses on the detection of trace amounts of heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Hg).
- Prohibited Materials Analysis within space and aerospace industry (ESCC Basic Specification 25500 -European Space Agency, ESA; and MIL-STD-1580 specification).
- Detection of counterfeit components according to the AS6171 standard issued by the SAE (Society of Aerospace Engineers).
- Positive materials identification. For instance, XRF is one of the techniques accepted by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) and ASTM International (American Society for Testing and Materials) to perform acceptant-test in combination with standard reference materials (SRMs).
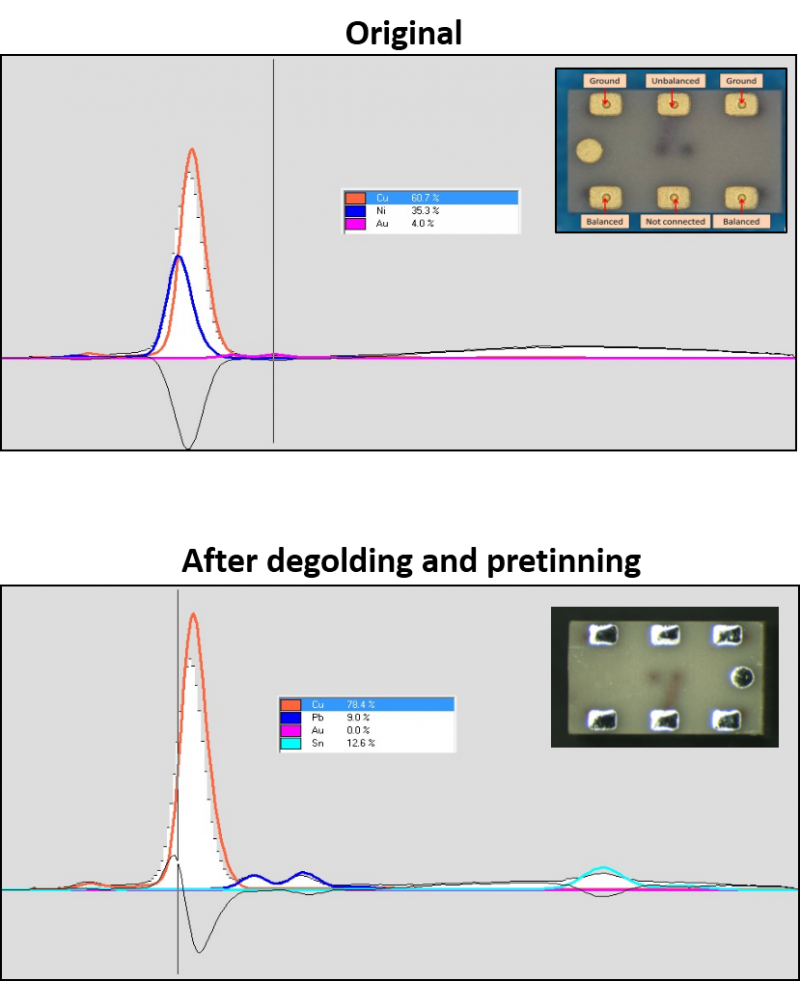
- Quality control processes; To illustrate this point the figure shows an XRF study performed at Alter Technology on of InGaP HBT terminals before and after Degolding + Retinning. In this case, the technique was used to asses the quality of the process within a failure analysis presented by our company at the 9thElectronics Materials & Processes for Space EMPS Workshop (Switzerland 2018).
How it works the XRF tool
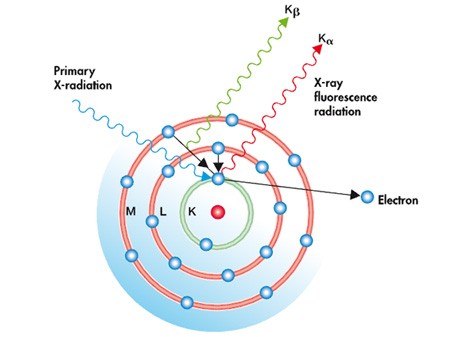
In this process, the atoms within the specimen are excited with a short-wavelength X-rays or gamma rays with a photon energy high enough to induce the ejection of tightly bound core electrons. As illustrated in the figure the generated inner vacancy is filled with an external bound-electron and the excess of energy is released (photon emission). The energy of generated X-ray photon (fluorescence) is determined by the energy of the involved electronic levels (see Kα and Kβ lines in the figure) which in turs depends on the nucleus characteristics.
Atomic model for the X-Ray Fluorescence Analysis method.
Contact us for more information
- Material Analysis Techniques for Electronic Components - May 6, 2022
- SAM: Survey to manufacturers and users - February 17, 2022
- What is a C-SAM Inspection? - January 29, 2022

0 comments on XRF tool, how it works and its applications in EEE parts