SAM: Main Issues in Plastic Encapsulated Systems
- Posted by Francisco Javier Aparicio Rebollo
- On November 17, 2020
- 0
Plastic Encapsulated COTS
Plastic Encapsulated offers:
- Lower procurement cost.
- Shorter procurement time.
- More performance and functionality available.
- Reduced size and weight.
An inherent risk of PEMs is related to:
- Lack of hermeticity.
- The mismatch with the thermomechanical properties of the inorganic internal part.

Definitions
Delamination: Lack of adhesion at the interface between different materials; typically between the molding compound and an internal inorganic part.
Crack: Fracture in the bulk or on the surface of a given material, either the molding compound or internal inorganic parts (for instance the die surface).
Void: Lack of material within the bulk for instance within the die attach or in the molding compound due to improper injection
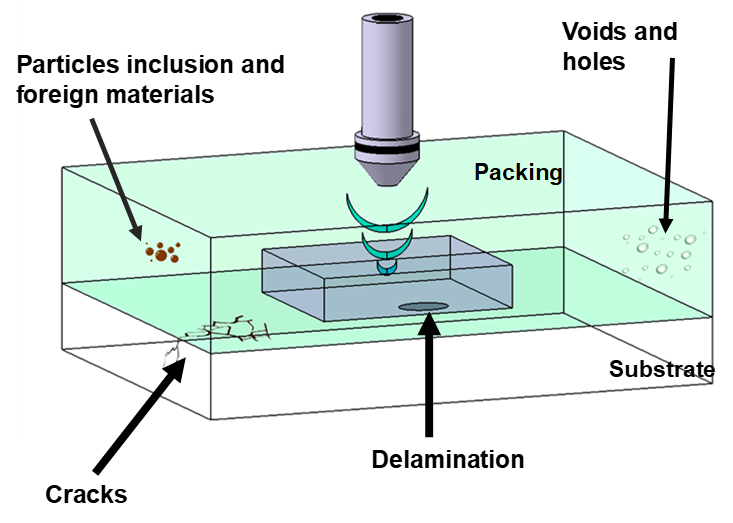
Lack of hermeticity
Contamination and moisture ingress and accumulation build-up result in metal corrosion. Occasionally, when the temperature rises, additional cracking occurs due to an effect known as popcorn cracking.
The actions that cause such contamination and accumulation of moisture are:
- Delamination on a surface breaking part
- Delamination on the die/paddle surface
- Cracks/void from the external surface to an internal feature
CTE Mismatch
Shear-induced damage of the die passivation produces metallic smearing (metallic tracks) and are caused by delamination on the die surface.
Bond wire degradation due to shear is connected by Cracks/void intersecting a bond wire.
Poor thermal dissipation is occasioned for Lack of adhesion or voids in the die attach.
Why Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM)?
- The ultrasound waves are extremely sensitive to density changes, so it is easy to detect any substantial change no matter how small.
- The best non-destructive approach for detection of air flaws in low-density materials
- With a sequential confocal inspection
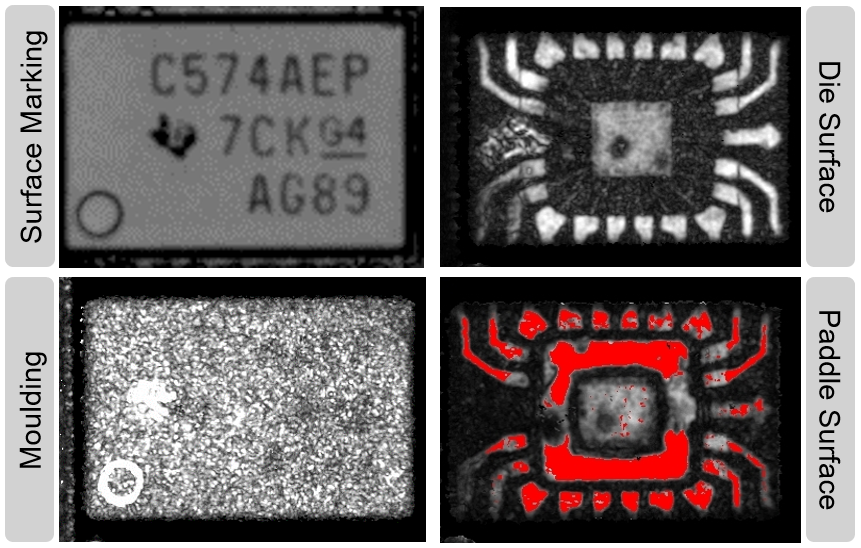
Test methods
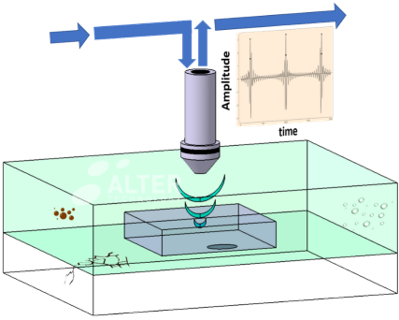
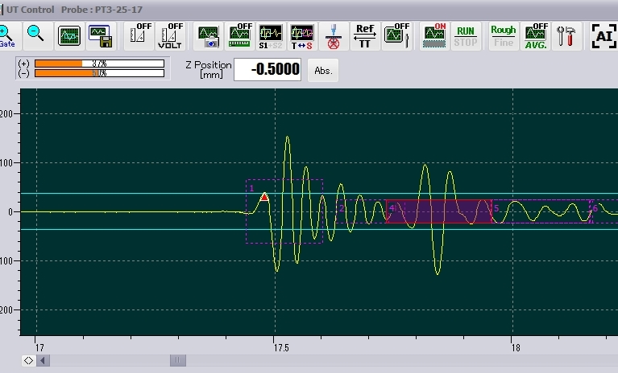
Detailed phase inversion analyses provide additional delamination contrast

ESCC 25200 Application of Scanning Acoustic Microscopy to Plastic Encapsulated Devices

PEM-INST-001 Instructions for Plastic Encapsulated Microcircuit (PEM) Selection, Screening, and Qualification

J-STD-020E Moisture/Reflow Sensitivity Classification for Nonhermetic Surface Mount Devices

MIL-STD-883 Test Method 2030 Ultrasonic Inspection of Die Attach.
MIL-STD-1580 Paragraph 16.5.1.3 Acoustic Microscopy
Although powerful, SAM is a complex inspection technique AND
- The different used specifications apply dissimilar rejection criteria
- Due to the high sensitivity to air flaws, on occasions, the impact of the observed deviations has to be assessed by additional test/s
- Verification procedures are not well specified in all the cases






In this context, Alter Technology has made an effort to clarify this scene and state a well defined internal procedure to address SAM findings:
- Historical review of our internal data accumulated for 30 years with different manufacturers and packages
- Survey to manufacturers and users about the most extended SAM test methods and verification procedures
- Detailed comparative analysis of the different SAM inspection methods
- Development of an internal making decision flow by considering all the involved factors
Contact us
Co-authors: David Ramírez-Cruzado Monge; Jose Cándido Vázquez, Dimas Morilla Mairen, Manuel Domínguez Álvarez, Antonio Rodríguez Arenas.
- Material Analysis Techniques for Electronic Components - May 6, 2022
- SAM: Survey to manufacturers and users - February 17, 2022
- What is a C-SAM Inspection? - January 29, 2022


0 comments on SAM: Main Issues in Plastic Encapsulated Systems