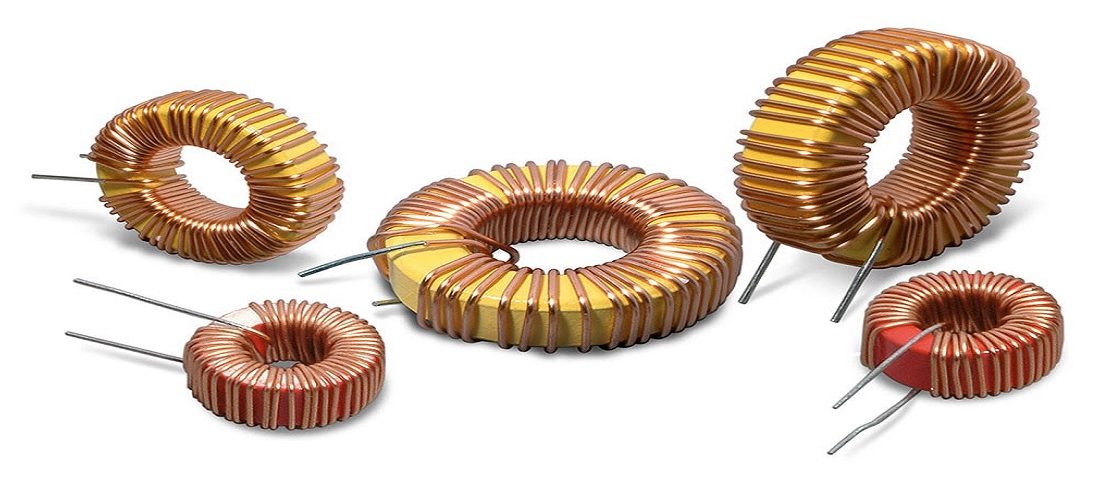
Storage Chokes and Power Inductors
- Posted by doEEEt Media Group
- On March 7, 2023
- 0
Switched-mode power supplies are becoming ever more widespread. The semiconductor manufacturers have contributed, offering a wide range of these integrated circuits with simplified circuit design. Care must be taken in selecting the appropriate power inductor storage choke to fully utilize the advantages of switching regulators.
This article is split into two chapters:
- calculation of power inductors
- example of high current inductor types
The selection of cores and windings of storage chokes are optimized for switching converters and DC-DC converters.
Leading manufacturers of storage chokes following recommendations from various switching converter IC manufacturers, e.g., National Semiconductor, Linear Technology, STMicroelectronics, Texas Instruments, Exar, Diodes, MPS, ON Semiconductor, Semtech, Maxim, and unique customized solutions can be found in their reference design guidelines.
Toroidal Core Types
From the EMC perspective, toroidal storage chokes are ideal: The magnetic field lines mainly pass through the core. The stray field and associated coupling in neighboring conductor tracks or components remain small.
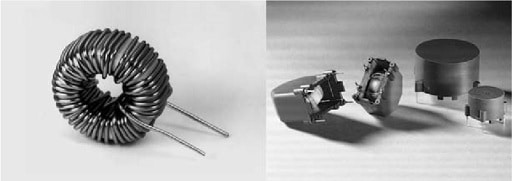
Figure 1. Toroidal storage choke (WE-SI and WE-GI)
In the field of switching converters, storage chokes serve to buffer electrical energy and, at the same time, to smooth the output current. The energy stored in the core in this process is:
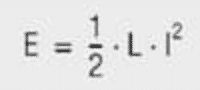
energy stored in storage chokes inductor eq. 1.
To enable high energy storage and minimize the resulting core losses, the toroidal core volume is divided into many electrically isolated regions. The iron powder used in our storage chokes, therefore, has three-dimensional, uniformly distributed, microscopic air gaps, which prevent eddy-current losses.
The disadvantage of reduced permeability is balanced by greater maximum energy storage and lower losses. Furthermore, these cores are extremely well suited for applications with high DC magnetization.
Data book specifications
Open-circuit inductance L0:
If the inductor is operated without DC pre magnetization or with only a small AC current, the open-circuit inductance L0 results. This value may be measured with sufficiently sensitive inductance measuring equipment for small AC voltages e.g. 0.1–0.5 V and a fixed measuring frequency between 1 kHz and 100 kHz, depending on the inductance value.
Inductance rating LN:
In addition to the small AC voltage amplitude, the specified DC current is superimposed, and the resulting inductance is measured.
Current rating IN:
The DC current, for which the inductance and wire thickness are specified and whose specifications are optimized. As shown in the graph in Figure 2., inductance only saturates with a much larger current.
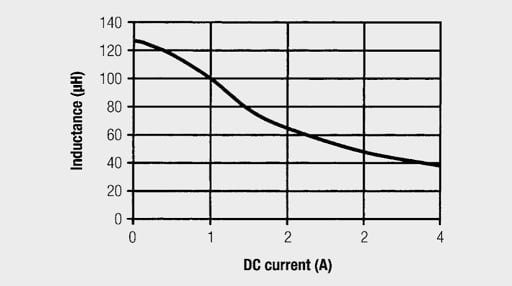
Figure 2. Inductance with DC pre magnetization; IN = 1 A; LN = 100 µH
DC resistance DCR:
The windings resistance value is measured with an ohmmeter at an ambient temperature of +25 °C. The test current for resistance measurement is a small DC current, which does not lead to a significant temperature increase in the wire. As values in the milliohm range are measured here, a 4-wire measurement must be made to minimize measurement errors.
Magnetic field energy E:
The energy for which the core data and windings of the coil is optimized. This is specified in microjoules. The following simple and practically proven formulae can be used for dimensioning a storage choke. A brief extract from the extensive core material program and the following table should provide an overview of the choke dimensioning process. Depending on the application, further specifications from the core material data spectrum may be necessary.
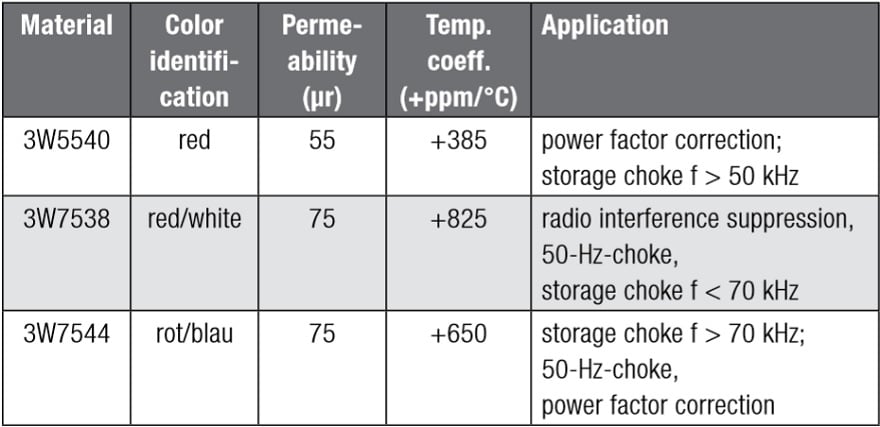
Table 1. Materials and their applications (source: Würth Elektronik)
Iron core material data:
Table 1. shows an overview of the most commonly used materials and their applications.
Operating temperature:
The operating temperature of the iron powder core may be from –55 °C to +125 °C. Prolonged core operation above +75 °C, however results in increased losses.
Insulation voltage:
The protective coating of the toroidal core uniquely identifies the core material, protects against environmental effects, and provides electrical isolation from the windings. Epoxy resin coatings are used, and an insulation dielectric strength of 500 VDC is achieved as standard. Higher insulation voltages can also be offered.
AL value: An AL value is specified for every size of the core to calculate the winding turns for the required choke; the tolerance is ±10%.
The standard means of measuring the AL value are B = 1 mT and f = 10 kHz.
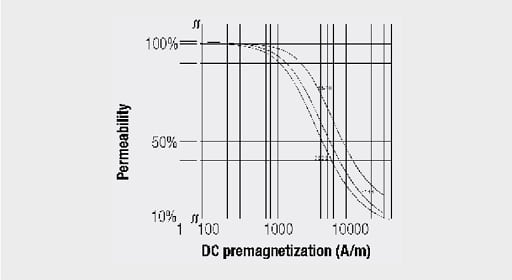
Figure 3. Effective permeability with DC premagnetization
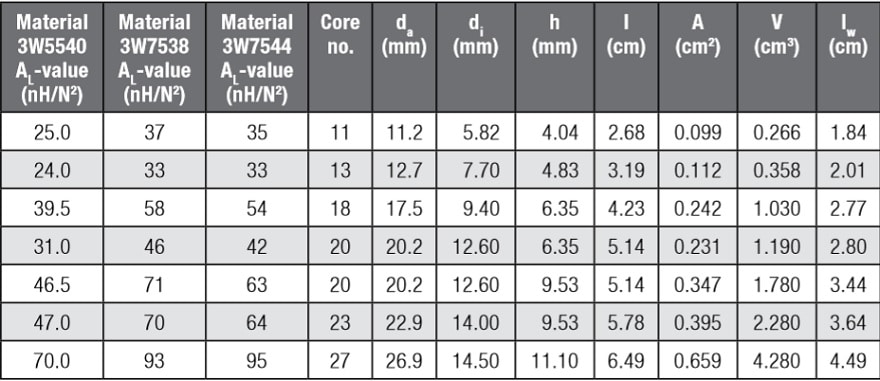
Table 2. Specifications of iron powder cores (source: Würth Elektronik)
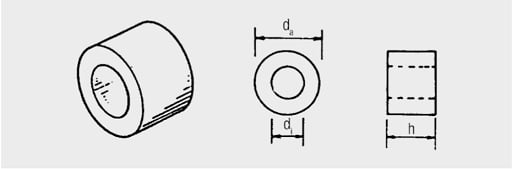
- da = outer diameter
- di = inner diameter
- h = height
- l = effective magnetic length
- A = effective magnetic cross-sectional area
- V = effective magnetic volume l
- W = winding wire length for 1 turn
Resources: EPCI Blog
- Space-Grade components available for immediate delivery - April 10, 2025
- Exclusive stock on doEEEt: How to access and request - April 10, 2025
- Managing EEE components for LEO and lower cost space missions - December 17, 2024


0 comments on Storage Chokes and Power Inductors