Magnetic Induction, Magnetic Flux and Faraday’s Law
- Posted by doEEEt Media Group
- On October 28, 2022
- 0
In vacuum and also with sufficient accuracy for air, this leads to:
![magnetic induction equation [4]](https://www.doeeet.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/magnetic-induction-equation-4.jpg)
magnetic induction equation [4]
The magnetic induction (BL) in the air for the above example is then given by:
![magnetic induction in air environment [5]](https://www.doeeet.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/magnetic-induction-in-air-environment-5.jpg)
magnetic induction in the air environment [5]
Magnetic Flux F
The magnetic flux (F) is the scalar product of the magnetic flux density (B) and the area vector (dA).
![magnetic flux equation [6]](https://www.doeeet.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/magnetic-flux-equation-6.jpg)
magnetic flux equation [6]
![magnetic flux equation in homogeneous field [7]](https://www.doeeet.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/magnetic-flux-equation-in-homogeneous-field-7.jpg)
magnetic flux equation in homogeneous field [7]
Faraday’s law
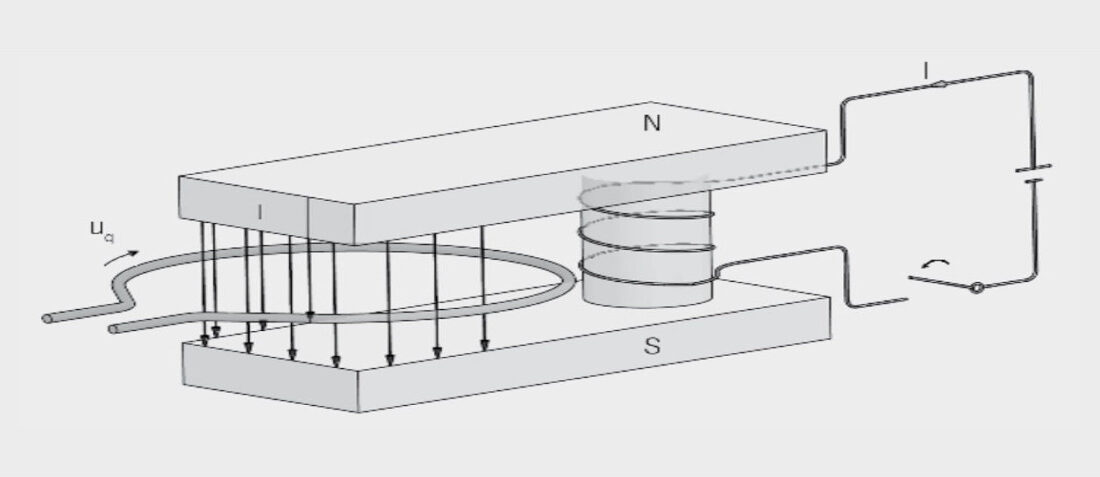
Up until now, we have considered static magnetic fields. If the magnetic flux changes with time, a voltage U is induced (Faraday’s law).
![induced voltage Faradys Law [8]](https://www.doeeet.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/induced-voltage-Faradys-Law-8-440x105.webp)
induced voltage Faradys Law [8]
t = time
The polarity of the voltage is such that a current is generated on closing a circuit whose induced magnetic field opposes the original magnetic flux, i.e. it tends to reduce the magnetic field (Lenz’s rule – Figure 1.).
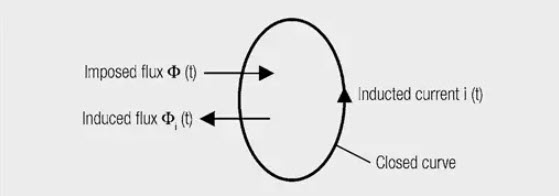
Figure 1. Representation of Lenz’s rule. The imposed magnetic field induces a current in the direction such that its induced magnetic field opposes the imposed field.
Taking a winding with N turns, Faraday’s law can be expressed in the following form.
![Faraday law with N turns winding [9]](https://www.doeeet.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Faraday-law-with-N-turns-winding-9.webp)
Faraday law with N turns winding [9]
l = length of the coil or of the magnetic circuit
I = current through the coil
L = inductance of the coil [H(enry) = Vs/A]
So the inductance limits the change in current once a voltage is applied. It can be calculated from the coil data:
![coil inductance equation [10]](https://www.doeeet.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/coil-inductance-equation-10-440x104.jpg)
coil inductance equation [10]
The energy stored in the magnetic field is subject to the following relationships:
![energy stored in magnetic field equation [11]](https://www.doeeet.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/energy-stored-in-magnetic-field-equation-11-440x74.jpg)
energy stored in the magnetic field equation [11]
The energy stored in volume V is composed of magnetic field strength H and the magnetic flux density B. For transformers and chokes with ferromagnetic cores, the flux density is limited by saturation and is constant throughout the magnetic circuit. If an air gap is introduced (material with permeability μ~1), the field strength is highest in this air gap with H = B/μ. It follows that the energy density is highest in the air gap. One also speaks of the energy being stored in the air gap.
- Space-Grade components available for immediate delivery - April 10, 2025
- Managing EEE components for LEO and lower cost space missions - December 17, 2024
- Filtering Characteristics of Parallel-Connected Fixed Capacitors in LCC-HVDC - November 21, 2024

![magnetic induction equation [1]](https://www.doeeet.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/magnetic-induction-equation-1-440x145.jpg)
![potential induced magnetic surge [2]](https://www.doeeet.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/potential-induced-magnetic-surge-2.jpg)
![magnetic field constant [3]](https://www.doeeet.com/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/magnetic-field-constant-3-440x138.jpg)

0 comments on Magnetic Induction, Magnetic Flux and Faraday’s Law