Leakage current characteristics of capacitors
- Posted by doEEEt Media Group
- On September 9, 2020
- 0
Capacitors, just like other electronic components, are constructed with imperfect materials. The imperfections and defects in these materials have significant effects on the electrical performance of capacitors. Some of the parameters determined by these defects and imperfections include impedance, dissipation factor, inductive reactance, equivalent series resistance, and leakage current. When designing an electronic circuit, it is necessary to consider these characteristics.
DC leakage current is one of the key characteristics to consider when selecting a capacitor for your design. Other important parameters include working voltage, nominal capacitance, polarization, tolerance, and working temperature.
Leakage current and its effects on the performance of capacitors
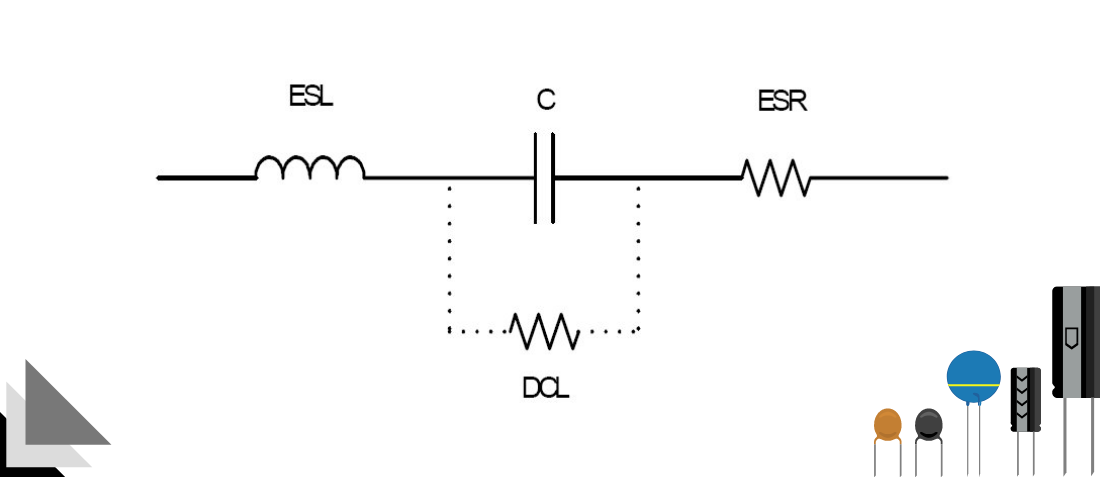
The conductive plates of a capacitor are separated by a dielectric material. This material does not provide perfect insulation, and allows current to leak through it. The DC leakage current refers to this small current that flows through a capacitor when voltage is applied. The value of this current mainly depends on applied voltage, capacitor temperature, and charging period.
The amount of leakage current varies from one type of capacitor to another, depending on the characteristics of the dielectric material and construction. Aluminium electrolytic capacitors have a large leakage current while ceramic, foil, and plastic film capacitors have small leakage currents. A very small leakage current is commonly referred to as “insulation resistance”.
In electronic circuits, capacitors are used for a wide range of applications including decoupling, filtering, and coupling applications. Some applications such as power supply systems and amplifier coupling systems demand capacitors with low leakage currents. Aluminium electrolytic capacitors and tantalum capacitors have high leakage currents and are generally unsuitable for such applications. Plastic and ceramic capacitors have lower leakage currents, and are commonly used for coupling and storage applications.
Dependence of leakage current on time
The leakage currents of some capacitors are dependent on time. At the instant the voltage is applied to an aluminium electrolytic capacitor, the current is at its peak. The occurrence of this peak current depends on the forming characteristics of a capacitor and the internal resistance of the source of voltage. When a capacitor is charged, its leakage current drops with time to a nearly constant value called operational leakage current. This small leakage current is dependent on both temperature and applied voltage.
Aluminium electrolytic capacitors have self-healing properties. The self-healing process has a significant effect on the leakage currents of aluminium electrolytic capacitors. Time dependence of leakage currents is also caused by forming of the dielectric material. Other parameters that determine the value of this small current include the type of electrolyte, capacitance, and forming voltage of the anode. The leakage current of a ceramic capacitor does not change with time.
Dependence of leakage current on temperature
The leakage current of a capacitor is dependent on temperature. The level of dependency varies from one type of capacitors to another. For aluminium electrolytic capacitor, an increase in temperature speeds up the rate of chemical reaction. This results in an increase in leakage current.
Compared to ceramic capacitors, tantalum capacitors have high leakage currents. The DC leakage current of a tantalum capacitor increases with an increase in temperature. The leakage currents of tantalum capacitors increase slightly when they are stored in a high temperature environment. This small increase in leakage current is temporary, and it is reversed by applying rated voltage for a few minutes. In addition, the leakage current of a tantalum capacitor increases slightly when the component is exposed to high humidity. Voltage conditioning helps to reverse this temporary increase in leakage current.
Ceramic and film capacitors have small leakage currents relative to electrolytic capacitors. For multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), the intrinsic leakage currents increase exponentially with an increase in temperature. The insulation resistance of a film capacitor is determined by the properties of the dielectric material. For this type of capacitor, an increase in temperature causes a decrease in insulation resistance and an increase in leakage current.
Dependence of leakage current on voltage
The DC leakage current of a capacitor is greatly dependent on the applied voltage. For aluminium electrolytic capacitors, this current increases with an increase in operating voltage. As the operating voltage exceeds the rated voltage and approaches the forming voltage, the leakage current increases exponentially. When the voltage applied to an aluminium electrolytic capacitor exceeds the surge voltage, the tendency towards temperature rise, electrolyte degradation, formation of excess gas, and other secondary reactions increases. Due to this reason, operating an aluminium electrolytic capacitor beyond the rated voltage is not tolerable. The DC leakage current of an aluminium electrolytic capacitor drops sharply when the applied voltage is decreased below the rated voltage.
The leakage current of an aluminium electrolytic capacitor increases when the component is stored for a long period of time. Such capacitors are restored to original characteristics through reconditioning. The process involves applying rated voltage to the capacitor for about half an hour.
For ceramic capacitors, the intrinsic leakage currents are greatly dependent on voltage. An increase in voltage results in a superlinear increase in intrinsic leakage current. The insulation resistance of a ceramic capacitor is independent of voltage.
Source: Capacitor Faks blog
- Miniature RF Connectors for high-performance testing - April 24, 2025
- Space-Grade components available for immediate delivery - April 10, 2025
- Managing EEE components for LEO and lower cost space missions - December 17, 2024


0 comments on Leakage current characteristics of capacitors