Capacitor Energy Content and Force
- Posted by doEEEt Media Group
- On April 1, 2024
- 0
The article describes capacitor energy content, what energy can be stored and delivered by the capacitor and what forces are present inside a capacitor.
Capacitor Energy Content
The energy stored in a capacitor can be described by equation:

……………[1]
Force action
from electromagnetic fields
Parallel current-carrying conductors are surrounded by magnetic fields exerting forces on each other. If currents flow in the same direction, the fields (and the conductors) attract each other. If the current flows in opposite directions, they repel each other.
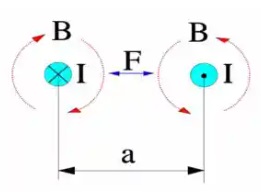
Figure 1. Magnetic force action, F, between conductors with a current flow, I. B = magnetic flux density.
If
- the conductor length l is expressed in m,
- the current I is expressed in A and
- the distance a is expressed in m,
the force per meter between the conductors will be

………………………[2]
According to the basic charge formula, Q = C x V (As). If we derive this expression, we obtain dQ/dt = I = C x dV/dt (A). Pulse loads are not unusual, especially in conditions with high voltage gradients, and thus, high charging currents also occur, which might cause appreciable magnetic fields between close lead patterns, for example.
Force action in electrostatic fields
Capacitors are typical applications where electrostatic fields are applied. These fields can generate significant mechanical forces. If we know the electrode distance d (m), it’s easy to determine the electric field strength E (V/m). Then, we can outline the force per unit area, i.e., the pressure that the electrodes exert on the dielectric.
……………………………….. [3]
Example. Suppose we have an oil impregnated paper capacitor with r = 5 and the dielectric = 15 m (0.6 mils) which is loaded with 250VAC. Then the instantaneous maximum pressure will be
0.1 kp/cm2 !
If we instead calculate on a 35 V solid tantalum capacitor with a typical and approximate dielectric thickness of 0.2 mm (0.008 mils) the formula gives at 30 V DC a pressure of
2 N/mm2 !
It is difficult to determine how much the dielectric is influenced by such forces, especially when the electrodes have such complex configurations. The electrostatic action of such forces is of vital importance.
Electrostatic Force Potential Impact
We learned in the article about the energy stored in the capacitor, but what is also important and demonstrated is that there is enormous mechanical pressure between the electrodes once voltage is applied.
This can be considered in failure analyses if we have a solid, sharp impurity within the capacitor dielectric – it may degrade the insulator not only by inducing electrical conductivity/increasing leakage current but also by causing mechanical damage to the dielectric due to the high electrostatic pressure between the electrodes. Hard and sharp micro-crystals in amorphous dielectric could be an example of such defects.
Resource: Blog EPCI
- Miniature RF Connectors for high-performance testing - April 24, 2025
- Space-Grade components available for immediate delivery - April 10, 2025
- Managing EEE components for LEO and lower cost space missions - December 17, 2024




0 comments on Capacitor Energy Content and Force