
Film Capacitor Technologies and Applications 2024
- Posted by doEEEt Media Group
- On September 5, 2024
- 0
Dennis Zogbi, Paumanok Inc., publishes on TTI Market Eye an outlook on film capacitors, their technologies, market, and applications.
This article analyzes the types, configurations and technologies for both AC film and DC film capacitors.
AC film capacitors include both small and large can polypropylene dielectric plastic film capacitors, including both dry and oil-filled designs, for use in electrical systems (motor run, microwave oven, magnetic ballast, power transmission and distribution, low voltage power factor correction, and specialty power film capacitors).
This article also focuses on DC film capacitors for printed circuit board applications in power supply, lighting ballast, automotive, and consumer AV applications. It includes 5mm pitch PET film capacitors, AC and pulse film capacitors, interference suppression film capacitors, and PPS, PEN, and PET film chip capacitors.
Additionally, the article offers the reader a look at the advantages and disadvantages of using specific types of plastic films, including PP, PET, PEN, PPS, PI, PTFE, and others, as capacitor dielectrics.
PLASTIC FILM CAPACITORS: TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW: 2024
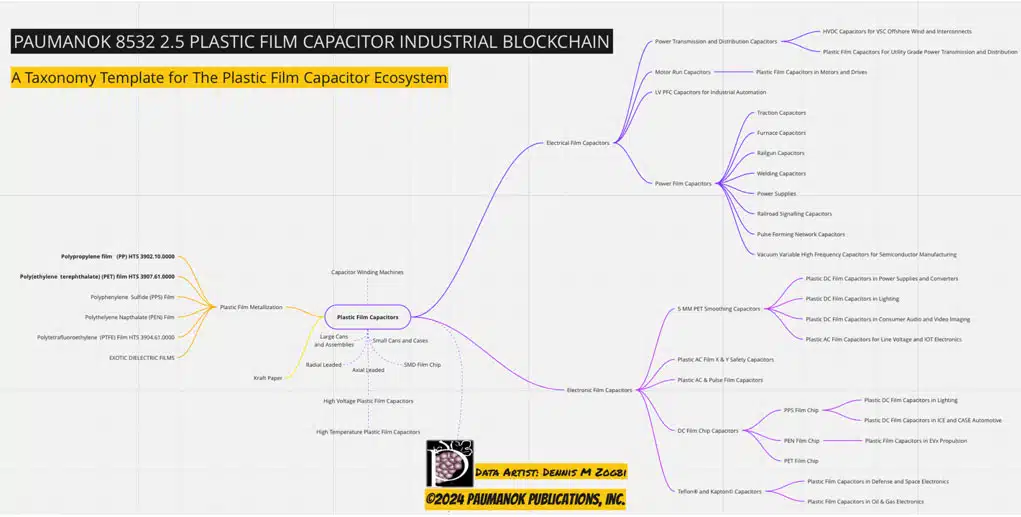
Figure 1.0 Mapping Out the Complex Plastic Film Capacitor Ecosystem for 2024; Source: ©2024 Paumanok Publications, Inc. All Rights Reserved
AC FILM CAPACITOR TYPES AND DEFINITIONS
The following list offers the reader a look at the different types, configurations, and technologies associated with electrical plastic film capacitors, also generally known as film capacitors. These capacitors are used to wound and stack plastic film, in many instances metallized film, as their primary dielectric material.
Power Transmission and Distribution PFC Capacitors:
High voltage power factor correction PFC capacitors are used in utility-grade power transmission and distribution systems where they are applied directly to the power grid to increase the efficiency by which power is transmitted and distributed – or, in other words – to correct the system’s power factor.
AC film capacitors used for power T&D applications are generally employed in circuits between 3kV and 745+kV. Distribution class capacitors are generally pole-mounted, outside plant applications from 3 – 15 kilovolts. In comparison, transmission class capacitors operate in both series and parallel to be used in power transmission systems to 745 kilovolts. These massive capacitors employ polypropylene film as their dielectric and are primarily manufactured by major companies that provide turnkey solutions to power utility companies worldwide.
Motor Run Capacitors:
Motor run capacitors are consumed in the global AC electric motor markets worldwide. The type of motors that consume motor-run capacitors are called split-capacitor motors, and the application of the capacitor is for power factor correction of the motor so that the motor will run more efficiently. Split capacitor motors are used in air conditioner compressor motors, refrigerator compressor motors and ceiling fans, and the annual success of the AC film capacitor market is generally tied to the annual success of the compressor motor market on an annual basis. The compressor markets are, in turn, largely tied to new housing construction worldwide.
Industrial Power Factor Correction Capacitors:
The low-voltage industrial power factor correction capacitor market is considered an extension of the high-voltage power factor correction capacitor market worldwide. However, the voltage requirements are lower than those of power T&D capacitors, and the customer base is also different. Also, the capacitor vendors are more diverse than those supplying the electric utilities with polypropylene capacitor banks. Capacitors consumed in low voltage power factor correction applications are rack or wall-mounted systems containing large can polypropylene capacitors in series.
The customer is usually a large corporation setting up a major manufacturing plant in the automobile, glass or chemical industries that will operate many large DC motors. In this application, the power coming into the plant must be consistent and efficient with limited transients to ensure quality manufacturing at the lowest possible electricity costs. The market driver to this industry segment is that some electric utilities offer incentives to manufacturers who demonstrate efficient power consumption, and the capacitors help them achieve their goals.
Lighting Ballast PFC Capacitors (Magnetic and HID):
Polypropylene film capacitors have been historically consumed in two markets in the lighting ballast industry: the power factor correction magnetic ballast business and the high-intensity discharge (HID) lighting business. However, the PFC market for polypropylene capacitors is declining as residential and business-class ballast manufacturers convert their production to electronic ballasts that do not use a polypropylene solution (they use a PET film capacitor or DC film capacitor solution instead).
The growth portion of the magnetic lighting business is for outside lighting due to the high voltages associated with parking lots and streetlights, making it a polypropylene PFC capacitor solution. So, overall, the lighting segment for polypropylene capacitors is declining as it is replaced by electronic ballast. However, there is still opportunity for growth in outside lighting, which is generally inefficient and is subject to updating on a worldwide basis (most outside lighting shines light skyward as opposed to the ground).
Microwave Oven Capacitors:
We tend to include microwave oven capacitors in the power capacitor segment; however, many suppliers view the market as a market by itself due to its distribution channel into residential home appliance markets. However, the capacitor application in a microwave oven is pulse discharge in nature and extremely high voltage, which qualifies it as a traditional pulse discharge capacitor. The microwave oven capacitor market is under tremendous price pressure globally due to the high rates of saturation of microwave ovens in established global economies. Therefore, most traditional manufacturers of microwave oven capacitors have abandoned the segment in favour of more profitable capacitor end-use markets.
Power Film Capacitors (Snubber, Commutation, Filter, Pulsed Power):
Power film capacitors represent the fastest growth businesses for AC film capacitors over the next five years. It is generally considered a basket category for a variety of AC film capacitor products that are finding good growth opportunities, primarily in renewable energy systems (wind, solar, HEV, ocean wave generation, hydrothermal), external defibrillators, variable speed drives, welding capacitors, furnace capacitors and traction capacitors for electric rail.
True power film capacitors are generally used for one of three applications: snubber capacitors, commutation or pulse discharge (which is why microwave oven capacitors are considered an offshoot of this segment). The most important aspect of this market is that the applications are unique and not considered power factor correction but used primarily for actuated burst power. The following capacitors are subsets of the power film capacitor dub category and are, in many instances, advertised separately by manufacturers of capacitors.
DC Link Capacitors:
Power Film capacitors are used in the DC link circuit for wind power generation, solar DC links, and as snubber capacitors to protect the IGBT semiconductors used in the control circuits. They are also used in the DC links in hybrid electric vehicles and emerging renewable energy systems such as geothermal and ocean wave generation technologies.
Traction Capacitors – Electric Rail Capacitors:
Power film capacitors are used in the DC link circuit in high-speed trains and mining rail systems.
Industrial Conveyor Capacitors:
Conveyor systems for manufacturing and baggage handling use variable speed drives that require power film capacitors.
Furnace Capacitors – Induction Heating:
Power film capacitors are used for burst power in industrial furnaces. This is a unique market segment.
Welding Capacitors – AAT:
Pulse/discharge capacitors are DC circuit capacitors that absorb or supply strong current surges. They are charged sporadically and briefly discharged about the charge time or vice versa. Discharge capacitors are subjected to high loads, high field strength corresponding to the required high energy density, and large peak currents because of the fast discharge, generating considerable mechanical forces in large capacitors and high AC voltages on inductive loads due to overshoot.
Power Smoothing Capacitors:
Smoothing capacitors are used to reduce the AC capacitor of pulsating DC voltage in measurement devices, control equipment and telecommunications infrastructure equipment, high voltage test instruments and cascade circuitry. These capacitors are predominantly DC in nature. Power supplies are used in a variety of applications and are predominantly AC/DC converters (70%) and DC/DC converters (30%).
- Power Supplies/Inverters/Converters/Chargers/UPS
- Telecom Infrastructure
- Battery Chargers (Auto, Industrial, Railroad)
- Ignition Speed Controllers
- Amplifiers
- Magnetizing Equipment
- Motor Drives
- Inverters
- Electric Vehicle Power Conversion
Additional Specialty Niche Markets for Power Film Capacitors:
Pulse capacitors find their niche in various forms of research & development for generating strong magnetic fields, for high-energy light flashes, high temperature, and high pulses of electrical energy (i.e., defence rail-gun and external defibrillator):
- Laser (Industrial and Medical)
- Defibrillator (External Use Only, Medical)
- X-Ray Machines (Pulsed, Laboratory, Medical)
- Ultrasonics (Pulse Welders, Cleaners, Industrial)
- Airport Runway Strobes (Pulse Forming Networks, Aviation)
- Railgun (Defense)
- Pulse Forming Networks (Radar, Aerospace)
- Missile Power Up (Defense)
- Food Sterilization (Commercial, Industrial)
- Marx Generators (Laboratory)
DC FILM CAPACITOR TYPES AND DEFINITIONS
There are four major sub-segments to the DC film capacitor markets worldwide. These include the 5mm metallized PET film capacitors, which are used for general-purpose smoothing in audio and video circuits, the AC and pulse speciality film capacitors, which are used in degaussing circuits for CRT monitors and some power supply and lighting markets, the interference suppression type for X and Y circuit applications (otherwise known as safety capacitors) and the DC film chip, which uses new ultra-thin dielectrics of PPS or PEN film and which are used for LCD backlighting and for power smoothing applications where volumetric efficiency is required.
General Purpose PET Film Capacitors (P5 Inductive):
The primary markets for general-purpose PET film capacitors are in TV and PC monitors and in lighting ballasts. Other applications are diverse but centre around consumer electronic applications, with an emphasis on consumer and car audio applications and switchmode power supplies. The P5 Inductive GP PET film capacitors account for the majority of demand.
Interference Suppression Safety Capacitors (X/Y):
International governing agencies such as Underwriter’s Labs (UL 1414 and 1283), Canadian Standards Association (CSA C22.2 No. 1 and No. 8), IEC (950 and 384-14), and European Community (EN60950 and EN32400) require that radio frequency interference (RFI) emanating from most electrical devices be limited to acceptable levels. The preferred method of limiting RFI is incorporating a film or a ceramic capacitor in line-to-line and line-to-ground applications.
There are two main types of interference suppression safety capacitors: the X and Y versions. These designations result from standards set by various international governing agencies mentioned in the introduction. In short, X capacitors are line-to-line capacitors used to suppress radio frequency interference in electrical systems. The Y capacitors are line-to-ground capacitors that suppress radio frequency interference in electrical systems.
Type X Capacitors: Otherwise known as line-to-line capacitors, these devices suppress radio frequency interference (RFI) in electronic systems and are placed between the main line and the neutral wires. X capacitors will generally have low capacitance values anywhere between 0.1 and 1.0µF
Class X1 Capacitors: The X1 type interference suppression capacitors are used in industrial computer or industrial lighting ballast applications. These are connected to a 3-phase line (connection to main power trunk lines within a building). An impulse of 4.0kV or higher must test these capacitors if their values are less than 1.0µF.
Class X2 Capacitors: This is the most common class of X2 capacitors because it is used in interference suppression applications when line voltages are from 150 to 250 VAC (nominal). This covers the suppression of interference on electrical and electronic devices connected to common AC wall outlets. On a global basis, this includes many products, such as personal computers, fax machines, hair dryers, and other common devices. These devices are impulse tested to 2.5kV if their values are 1.0µF and less.
Type Y Capacitors: Otherwise known as line-to-ground capacitors, these capacitors are placed on the line leading from the main line to the chassis ground or on the neutral line to the chassis ground. Y capacitors have small capacitance values to limit the 50 or 60Hz leakage current to the ground. The 4700 pF type Y capacitor is a common value.
Class Y1 Capacitors: The Y1 type of capacitor is suitable for line voltages up to 250 VAC and is impulse-tested up to 8kV. The application is usually when the requirement for bridging double insulation (or reinforced insulation).
Class Y2 Capacitors: This is the most popular type of Y-class interference suppression capacitor. It bridges basic and padded insulation with line voltages up to 250 VAC. The primary application is in power supplies used in personal computing equipment. These devices are impulse-tested to 5kV.
AC and Pulse Film Capacitors:
AC and pulse film capacitors are used in high voltage applications where extremely low dissipation factors, very small inherent temperature increases, high pulse environment and resistance to corona are required. The environments in which AC and pulse capacitors are required include television set deflection circuits in cathode ray tube type designs, including the important flyback and S-correction (hold) circuits, electronic ballasts, switch mode power supplies (SMPS) and other applications where high current and high frequency are factors of the electronic system. AC and pulse capacitors require high voltages and comparably low capacitance values. Typical voltages are 250 to 2000Vdc (or 160 to 600VAC) with capacitance values from 0.001 to 3.3µF. Because of the high voltage requirements, polypropylene dielectrics are used.
Moreover, since high voltages and low capacitance values are required in the applications where AC and pulse capacitors are used, the dielectric selection is limited to electrostatic capacitors, such as film and ceramic capacitors. Film is preferred in television sets, ballast and SMPS applications because of its “self-healing” properties. AC and pulse film capacitors are almost exclusively radial leaded, box-type capacitors with dielectric and lead-type variations. Dielectrics are typically metallized polypropylene, double metallized polypropylene or film/foil constructions where the film is polypropylene and the foil is predominantly tin, copper or aluminium.
In television and PC monitor applications, set designers generally prefer to employ metallized PP film and foil constructions in S-correction and flyback transformer applications. However, recently, we have noted a trend towards metallized and double-metallized PP film constructions for the S-correction application. This trend, however, does not affect the flyback transformer application, which remains film/foil.
Unfortunately, AC and pulse film capacitors are not required for LCD monitors; therefore, they have undergone and will continue to undergo a substantial drop in demand from display manufacturers as they convert their production output from CRT to flat panel display. The remaining demand will become increasingly competitive with substantial price reductions and a smaller overall value market going forward.
SMD Film Chip:
To prevent the switchmode power supply filtering market from migrating away from standard 5 mm PET film capacitors to surface mount multilayered ceramic chip capacitors, the film capacitor industry has invested millions of dollars in the development of a film chip capacitor that has the following attributes:
- Readily Surface Mountable
- Withstands Soldering Temperatures
- Priced by Leaded Versions
PLASTIC DIELECTRICS
There are many plastic dielectrics because of the ease of manufacturing metallized film into capacitors through machine winding. Polypropylene and polyester terephthalate are the two primary plastic dielectrics. However, there are eight additional metallized film variations. See Figure 2.0.
- PP-Polypropylene: This dielectric is associated with all “electrical” systems. The metallized PP film versions are for applications in motor run, X&Y circuits, snubber capacitors, and pulse discharge applications. However, there are also hazy PP film markets in power transmission and distribution capacitors.
- PET-Polyethylene Terephthalate: This dielectric is used in metallized capacitors and is designed for high voltage applications in line voltage equipment such as monitors, power supplies, and lighting ballasts.
- PEN-Polyethylene Napthalate is a dielectric for capacitors that is available in standard and high-voltage configurations. It is a niche for chip film capacitors and is consumed primarily for backlighting in monitors and screens.
- PPS-Polyphenylene Sulfide: This is a high-temperature dielectric film used in chip format for automotive and industrial applications.
- PI-Polyamide: An alternative to PTFE for space applications.
- PS-Polystyrene: An alternative to polycarbonate for defence, mil-spec alternatives and industrial variants.
- PTFE-Polytetrafluoroethylene: A specialty plastic dielectric film consumed in space capacitor applications.
- PC-Polycarbonate: A rare dielectric film with a MIL-SPEC. Hard to manufacture.
- PVDF-Polyvinylidene Fluoride: A rare dielectric film used for pulse discharge applications.
- Siloxane: A rare or emerging high voltage dielectric plastic film.
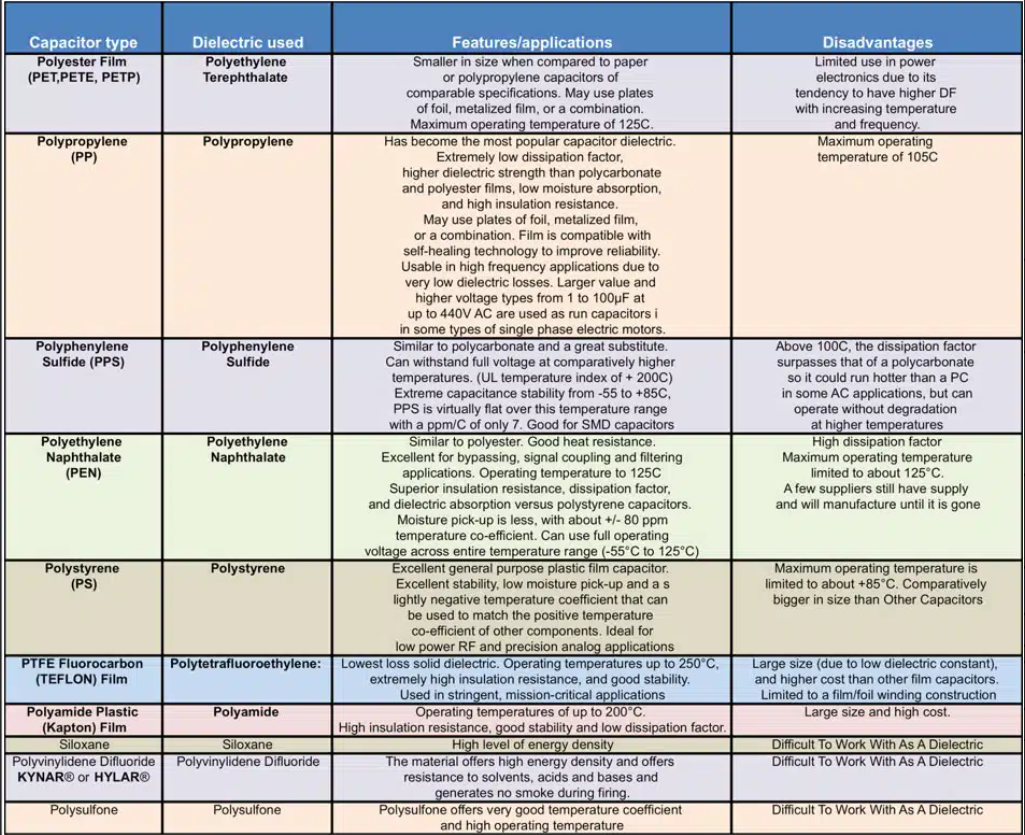
Figure 2.0 Advantages and Disadvantages of Plastic Film as a Capacitor Dielectric for 2023; Source: ©2024 Paumanok Publications, Inc. Compiled from Multiple Sources
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
The global market for plastic film capacitors is complex and highly fragmented, representing more than 100 manufacturers worldwide. It is broken down into multiple product types, configurations, and types of dielectric film, which comprise a vast, versatile, and highly unique ecosystem.
- Space-Grade components available for immediate delivery - April 10, 2025
- Exclusive stock on doEEEt: How to access and request - April 10, 2025
- Managing EEE components for LEO and lower cost space missions - December 17, 2024

0 comments on Film Capacitor Technologies and Applications 2024