Role of COTS in the COM Strategic Research and Innovation Agenda for Space
- Posted by Fabio Vitobello
- On December 3, 2019
- 0
EU Space Strategy
In 2016, the European Commission published a Space Strategy for Europe with the objectives:
- maximizing the benefit of space for society and EU economy
- Fostering a competitive and innovative European sector
- Reinforcing Europe’s autonomy in accessing and using space
- Strengthening Europe’s role as a global actor
The Space Programme proposal for 2021-2027 includes four components:
- Galileo/EGNOS
- Copernicus
- Space Situational Awareness (SSA)
- Secure Governmental Satellite Communication (GOVSATCOM)
Space R&D activities within the Horizon Europe proposal will support:
- R&I needs of the Space Programme
- competitiveness of the EU Space sector primarily through space technology development.
A changing Space…
- Since the beginning of the 90s private customers emerged progressively
- 33% of the mass launched in 2017 was for private customers
- Growth of the number of launches of micro and nanosatellites
- Over the last 7 years: 43% of spacecrafts launched are below 10kg
- Strong trend in the use of large constellations, many declared projects:
- OneWeb, Google/SpaceX, Samsung, LEOSat, TeleSat, Commsat
- Iridium Next, Norstar, LEOsat, Galileo, TerraBella, Jilin
- PlanetiQ, UrtheCast, Laserlight…
New Space Practices
- New Space practices, particularly evident in constellations, based on
- Target very low cost
- Modularity, no modification allowed – use as is
- Go fast, fail quick, restart
- Large series production methods, robotic assembly, supply economies
- Share common resources – RF spectrum, access to space…
- Acceptance of higher risks
- Systematic use of COTS
Using COTS in Space is not just a pick and place exercise, a structured approach is necessary
Critical elements
- Limited traceability
- Limited access to qualification and supply chain data
- Unless parts qualified based on Automotive standards e.g. AECQ100
- Unknown radiation performance
- Testing and screening is mandatory
- Product turnover, process changes, obsolescence
- Lead-free terminations
- Sensible aspect considering that the REACH regulatory pressure may result on difficult market availability of leaded solder paste and coatings
In return, very low cost if compared to a space qualified part
Strategic Research and Innovation Agenda
- Guidance and recommendations for Space Research in Horizon Europe
- Consultation of a broad base of stakeholders
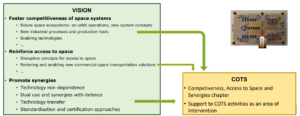
How COTS are seen by the SRIA?
Technology Transfer, Manufacturing, Assembly and Testing at larger-scale
Need to enhance the coordination and create synergies by sharing technologies between space and non-space sectors
- Best use of COTS components as a response of spin-in activities from non-space
- Prospecting, promoting, demonstrating and qualifying technologies developed for other markets
HOW?
- Prospective of funding for projects aiming at bringing COTS components into Space applications
- Support to specific actions aiming at:
- Evaluating compatibility of aeronautics, automotive, commercial parts with Space requirements
- Building a shared European industrial knowledge
Time line for COTS in Space Research and Conclusions
- In 2020 the preparation of the Horizon Europe Space Work Programme based on the SRIA will take place
- Place holders were introduced in the SRIA covering many aspects of the Space Research including also the use of COTS
- What shall we do first, what will be the priorities?
- This conference and other discussions that will take place in the next months will be considered for deciding the priorities
- Role of COTS in the COM Strategic Research and Innovation Agenda for Space - December 3, 2019

0 comments on Role of COTS in the COM Strategic Research and Innovation Agenda for Space