CSAM Techniques for COTS Validation
- Posted by Francisco Javier Aparicio Rebollo
- On December 3, 2019
- 0
This presentation shows the non-destructive detection of air flaws (delamination, voids and cracks) and related critical failures in plastic packing for COTS validation: The Scanning Acoustic Microscopy technique, inspection zones and typical failure modes and ALTER SAM capabilities.
SAM Inspection for COTS validation
Outline
- Introduction
- The Scanning Acoustic Microscopy technique
- Inspection zones and typical failure modes
Introduction
Plastic Encapsulated COTS offers:
 Lower procurement cost
Lower procurement cost- Shorter procurement time
- More performance and functionality available
- Reduced size and weight
- ATN SAM capabilities
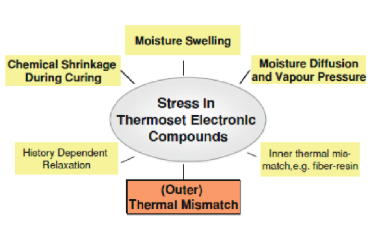
Inherent risk of PEMs is related to:
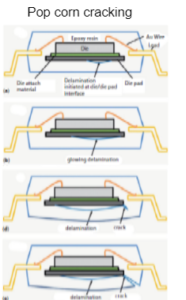 Lack of Hermeticity (high internal vapour pressure)
Lack of Hermeticity (high internal vapour pressure)- Stress build-up in plastic encapsulated systems
Main anomalies in plastic packages
- Delamination: Lack of adhesion at the interface between different materials; typically between the moulding compound and an internal inorganic part
- Crack: Fracture in the bulk or on the surface of a given material, either the moulding compound or internal inorganic parts
- Void: Lack of material within the bulk for instance within the die attach or in the moulding compound due to improper injection
Main package defects involve air/solid interfaces
Failure modes
Delamination voids and cracks are the root case for different failure modes
 Poor mechanical stability
Poor mechanical stability- Permanent or intermittent electrical opening
- Inefficient heat dissipation
- Metal corrosion
- Cracking or fracture of die or encapsulant
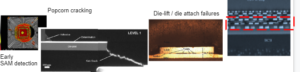
Why Scanning Acoustic Microscopy for COTS validation?
Ultrasound waves are extremely sensitive to density changes
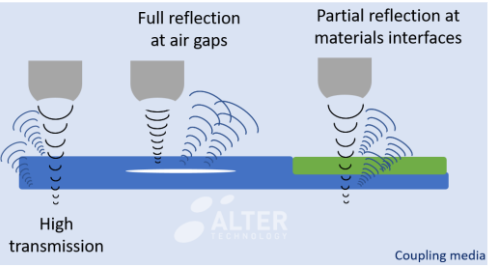
The intensity of the reflected beam is used for the detection of materials interfaces
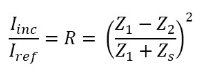
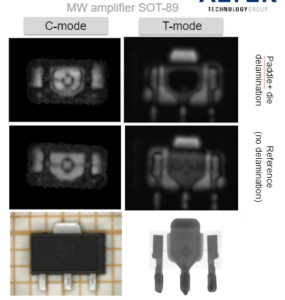
Scan modes
C-mode: The intensity of the reflected beam at a given depth is analysed to reconstruct the internal structure
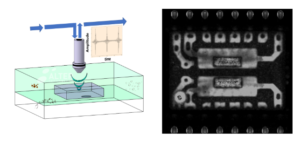
Imaging of internal structures with confocal resolution
Peak amplitude analyses are used for the detection of interfaces between different materials/media
Phase analyses are used for the identification of air flaws (delimitations)

A-scan: Detailed analysis of the A-scan provides the most reliable results for the detection of delaminated areas
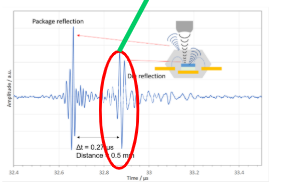
SAM non-destructive approach the early detection of critical failures in plastic encapsulated systems
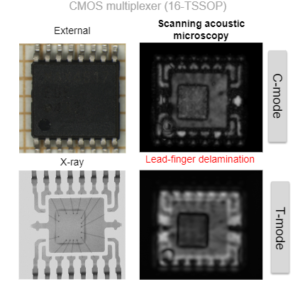
External
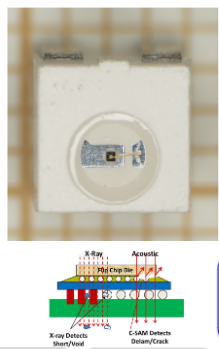
X-Ray
High lateral resolution
- Wire deformation
- Voids
- …
SAM
High sensitivity to air gaps
- Delamination
- Cracks
- Voids
Test methods

J-STD-020E Moisture/Reflow Sensitivity Classification for Non-hermetic Surface Mount Devices
PEM-INST-001 Instructions for Plastic Encapsulated Microcircuit (PEM) Selection, Screening, and Qualification
ESCC 25200 Application of Scanning Acoustic Microscopy to Plastic Encapsulated Devices
MIL-STD-883 Test Method 2030 Ultrasonic Inspection of Die Attach
MIL-STD-1580 Paragraph 16.5.1.3 Acoustic Microscopy
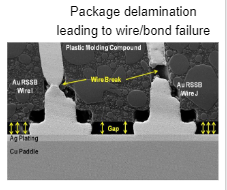
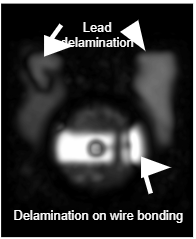
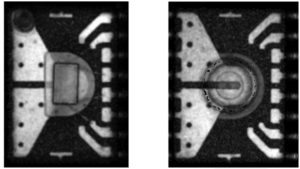
Critical delamination sites in leaded packages
Bonding areas
Failure examples
Delamination on bonding areas
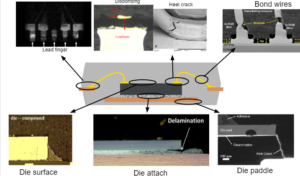
 Main reliability issues
Main reliability issues
- Shear stress over wire bonds
- Disbanding
- Heel cracking
- Stitch crack in wires
- Bonding corrosion
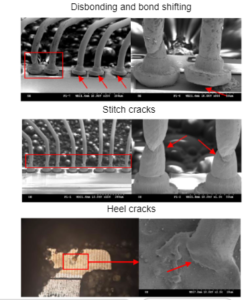 Main reliability issues
Main reliability issues
- Shear stress over wire bonds
- Disbanding
- Stitch crack in wires
- Heel cracking
- Bonding corrosion
- Wu et al. 2014 International Conference on Reliability, Maintainability and Safety (ICRMS)
- Cai et al. 17th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology 978-1-5090-1396-8/16/$31.00 ©20161EEE
 Main reliability issues
Main reliability issues
- Shear stress on die surface and bondings
- Cracks at the passivation layer
- Damaged metallization
- Degradation of the contact bridges

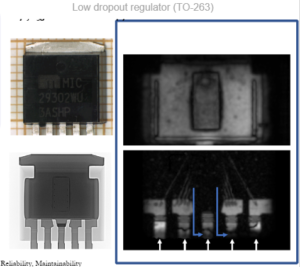
Voids in die attach
Main reliability issues![]()
- Poor mechanical stability
- Inefficient heat dissipation
Delamination of surface breaking parts
 Reliability issues
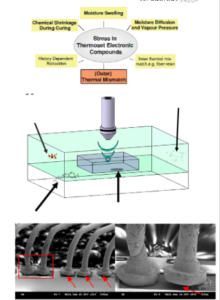
Reliability issues
- Path for moisture and contamination
- Secondary cracking phenomena
- Corrosion at active area

Detection of latent failures
SAM is used for COTS validation to an early detection of latent critical failures

 Summary
Summary
Plastic encapsulated system experience high internal stress
They promote the development of internal structural anomalies
They are the root cause of different failures modes in ICs
SAM is the most effective tool for the non-destructive detection and screening of such deviations

ALTER SAM capabilities
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy is a complex technique:
REQUIREMENTS FOR A SUITABLE INSPECTION
- Specialized and dedicated staff
- Advanced characterisation systems with flexible inspection capabilities adapted to the architecture of the specimen
- Multi-scan based interpretation in case of suspicious results
- Comprehensive multi-depth inspection of critical parts within thick packages
ALTER TECHNOLOGY SERVICES
- Teamwork formed by Ph.D. in Materials Science experienced Engineers and qualified technicians
- Recently upgraded system equipped with the state of the art features.
- The final result is based on the combined assessment of A-mode, confocal C-mode and Through-transmission scan modes
- Prelaminar X-ray inspection is systematically conducted to identify the critical focal planes for multifocal C-SAM inspections
Recently upgraded capabilities
 FineSatV (Hitachi)
FineSatV (Hitachi)
- Fast inspection speed
- High-quality images
- Recently developed operating software with novel analysis functions.
- Simultaneous confocal c-mode and through-transmission inspections
- Advanced Fourier-transform data-treatment
- Wide variety of transducers (adjustable inspection depth/lateral resolution).
-
-
- Maximum lateral resolution 30 μm.
- Maximum inspection depth 5 mm or higher depending on the density
-
-
Scan modes
T-mode: The intensity of the ultrasound beam transmitted by the system is used to prove the internal structure
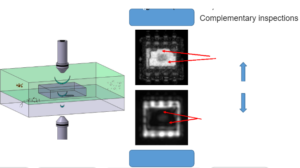
Additional scan modes
B-mode
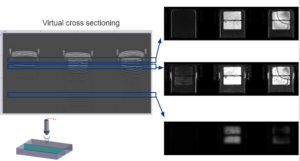
 Depth mapping capabilities
Depth mapping capabilities
- Constructional analysis verification
- Measurements of defects location (depth).

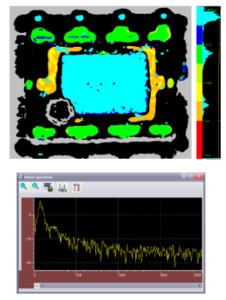
Fourier transform data treatment
Used to improve image quality
Inspection procedure
Confocal C-SAM Through-mode
A-scan is systematically registered along the whole sample for all the inspected parts
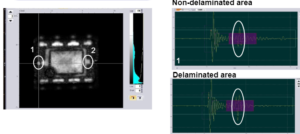
Full area A-scan is available after inspection
Upon request they can be provided to the customer for the areas of interest.
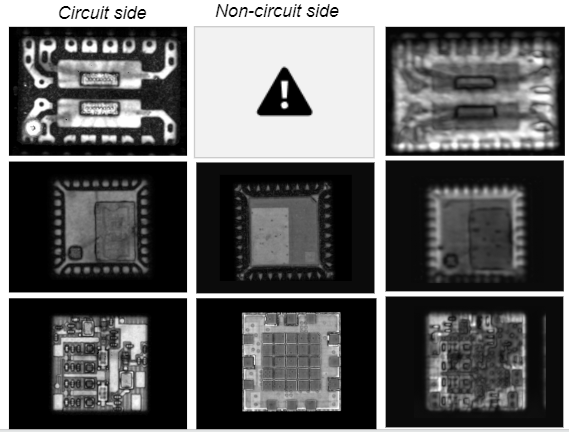
Multi-depth confocal inspection
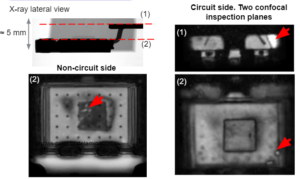
Reliable interpretation of active part features
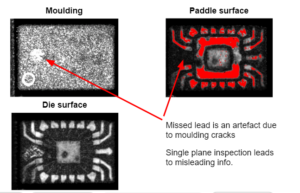
High quality images (1500×1500 pixels resolution) are registered for each specimen, scan mode and inspection plane
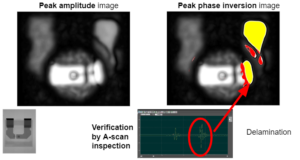
Specific phase-inversion analysis-software is used to detect and mark air interfaces and related defects
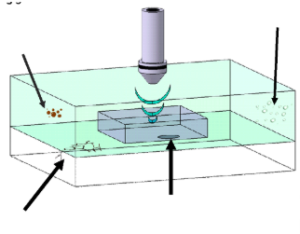
Conditioning (drying) of non-destructive samples
Inspection must be conducted in a liquid coupling media, typically water
Specifications MIL-STD-883, J-STD-020E and
J-STD-033 (Handling, Packing, Shipping and use of Moisture Reflow and Process Sensitive Devices) state the procedures to remove absorbed humidity before shipping and/or soldering
Very gentle drying process agreed with the customer is used to remove moisture absorbed in the plastic package
Typical baking conditions range from 90 ºC to 125 ºC for 48 h to 24 h depending on the temperature
Complementary inspection capabilities

- Material Analysis Techniques for Electronic Components - May 6, 2022
- SAM: Survey to manufacturers and users - February 17, 2022
- What is a C-SAM Inspection? - January 29, 2022


0 comments on CSAM Techniques for COTS Validation