SEL protection for Space Applications
- Posted by Sonia Vargas
- On June 14, 2020
- 4
SEL Protection For Space Applications: Use and Evaluation of Current Limiters
There are several strategies in order to protect circuits from Single Event Latch-Up. Implementing such protection with Current Limiters is a versatile and programmable option. However, this part types must be evaluated under certain stress sources related to space applications, where a set of electrical parameters are measured during the process. Here are presented the typically used ones.
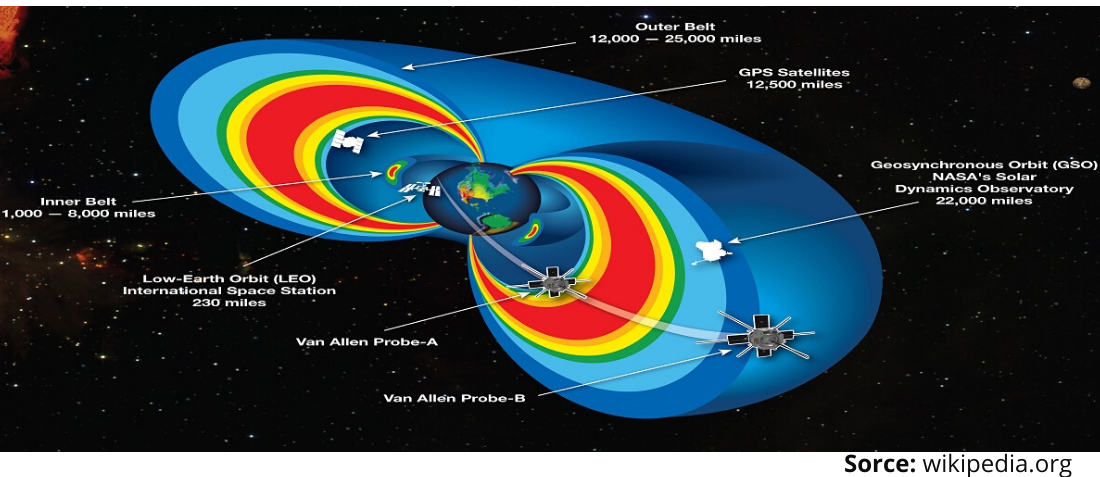
Single Event Latch-Up (SEL) is a condition where a low impedance path is created between a supply pin and ground. This condition is caused by a trigger such as a single ionizing particle (heavy ions i.e. alpha particles, protons, neutrons and high energy protons). The main problem is that once activated, the low impedance path remains even after the trigger is no longer present. This low impedance path may cause system upset or catastrophic damage due to excessive current levels. The Latch-Up condition typically requires a power cycle to eliminate the low impedance path.
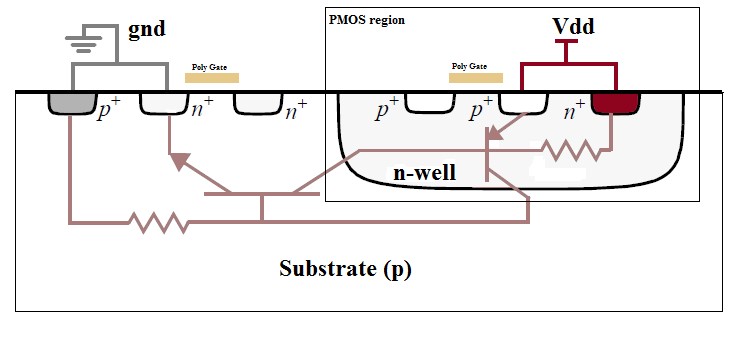
CMOS and BiCMOS technologies are susceptible to this phenomenon, as NMOS and PMOS transistors are used to create the circuit functions. In the design of the CMOS integrated circuit, the proximity of the PN junctions that form the NMOS and PMOS transistors create inherent parasitic transistors and diodes. These parasitic structures create PNPN Thyristors, also called silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs).
Latch-Up is not a breaking risk if the voltage and current levels applied to the device adhere to the absolute maximum ratings at the same condition (e.g. DC), but must be deactivated turning off the power supply under a certain time of reaction to properly restore the original circuitry performance.
In order to solve this issue, current limiters can be used. However, depending on the circuitry to be protected, several parameters evolution under stress must be monitored for its use in space applications, as example:
Current Limit: This can be measured by an external precision resistor where the power supply current is flowing, connected to the current limiter with Kelvin connections for highest accuracy. The current limit to switch off is adjusted by the value of this resistor. The detector will be triggered by a certain exceed of voltage drop in such resistance. The proper functional reaction to voltage changes must be measured.
Trip-Off Time: When an overcurrent event occurs, the device will start the trip-off timer. The devices can start to apply a current limit and after the configured trip-off time (set by an external resistor and/or capacitor) the power supply is turned off.
Recovery Time: If the current limiter has a re-triggerable mode, if the duration of the overcurrent is greater than the trip-off time, the switching off stays during a configurable time (set by an external resistor and/or capacitor) until the power supply is restored again.
- Typical Parameters in the Electrical Test of Operational Amplifiers - December 28, 2020
- SEL protection for Space Applications - June 14, 2020
- When and What to do in an Electrical Test - February 21, 2020

4 comments on SEL protection for Space Applications