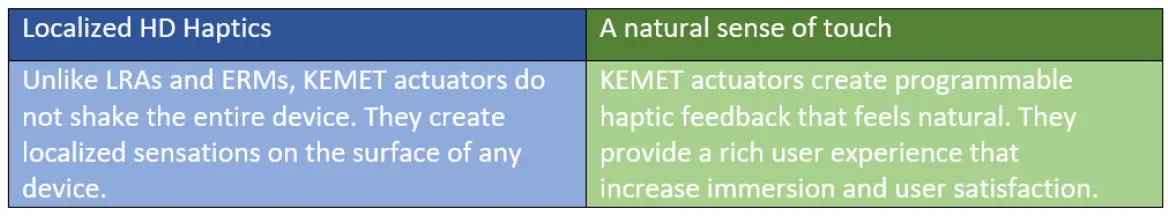
The wide bandwidth of the devices coupled with some physiology of touch and sensation allows for a very innovative haptic response rather than the simple on/off, buzz, or no buzz notifications associated with ERMs.
Possibilities With Piezoelectric Polymers
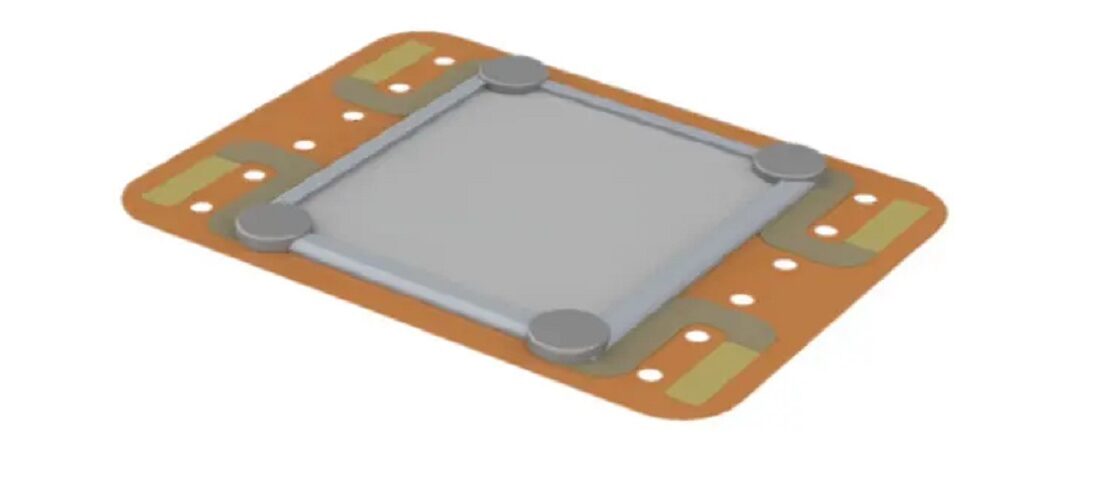
The EMP KEMET thin actuators are made from a unique electro-active polymer film that delivers piezoelectric effects…mimicking the sense of touch. They can convey specific material textures and familiar feelings, like the clicks and clacks of buttons, and more. In an unpowered state, the molecular structure of the film is aligned randomly. When powered, the molecules align in a direction that elongates the film, creating the piezoelectric effect.
Bonding or integrating the actuator to a rigid substrate transforms actuator elongation into an out-of-plane vibration, creating the haptic effect. Because the integrated haptic devices vibrate over a wide range of frequencies, the user experience is enhanced. First, rich, low frequencies provide pleasant sensations, and then higher frequencies impart the detail and overtones, creating effects with unusually natural sensations.
Applications
EMP technology is making history by providing a sense of touch in many consumer electronic devices’ user interface.
In gaming controllers, the haptic sensation enhances the experience to a whole other level. With EMP actuators being very fast, there is no lag between the visual and haptic sensations.
In the case of AR/VR applications, visual and audio already exist. However, the heightened sense of touch delivered via EMP actuators through various outputs allows the user to distinguish between different objects by touching them and feeling the difference.
In industrial applications, KEMET actuators combined with capacitive touch can create intuitive and easy-to-use Human Interface control systems.


0 comments on How Work the Advances in Piezoelectric Haptic Sensors?