The application of laser SEE testing as a new radiation effects validation and screening technique for COTS components
- Posted by Richard Sharp
- On December 3, 2019
- 0
Cobham RAD Europe Ltd
- Our Harwell, UK office provides services in:
-
- Radiation testing for space, nuclear and medical applications
- Electronic component and materials testing
- Total integrated dose (TID) testing (ESCC 22900, Mil-Std-750/883)
- Single event effects (SEE) testing (ESCC 25100, JESD57)
- Irradiation with gamma rays, electrons, protons, neutrons, alpha particles and heavy ions
- SEREEL2 laser single-event effect test systems
-
- We have our own, walk-in cobalt cell for gamma irradiations
- ISO 9001:2015 accredited
- We are the only test house outside the US to have full DLA laboratory suitability for total dose testing over all test conditions
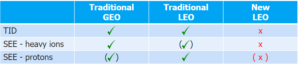
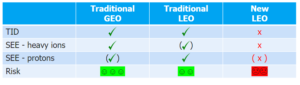
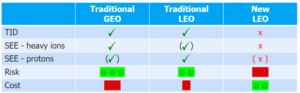
Current practice for space radiation testing
What is laser SEE testing?
- Single Event Effects (SEE) are prevalent in space, for aerospace applications and even at ground level
- Transistor dimensions have been scaled sufficiently that most digital devices are now sensitive to SEE unless mitigated
- The cost of testing at accelerators is high and availability is poor
- The confluence of these factors now makes laser SEE testing attractive
- Single Event Effects (SEE) are prevalent in space, for aerospace applications and even at ground level
- Transistor dimensions have been scaled sufficiently that most digital devices are now sensitive to SEE unless mitigated
- The cost of testing at accelerators is high and availability is poor
- The confluence of these factors now makes laser SEE testing attractive
- Pulsed lasers enable the charge to be injected into semiconductor structures to mimic an ion strike
- Excellent temporal and spatial information is available
- Testing is quick and low cost
- Ideal for screening and product development
Pros and cons
- Pros
- 24/7 availability in your lab
- Low cost
- SEE response can be related temporally and spatially to the sample
- No radiation damage is imparted to the sample
- Cons
- No general quantitative correlation with ion beam testing
- The laser beam cannot penetrate metal layers
- Only complementary to radiation testing
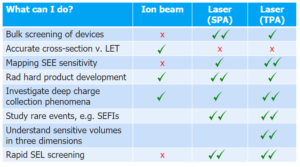
Applications
Key features for laser SEE testing
- Stability of the laser (users want no adjustments)
- Friendly user interface
- SPA and TPA capability in one machine
- Easy set-up (auto-levelling, autofocus, automatic die registration)
- Flexibility to accept a wide range of DUT board size and mass
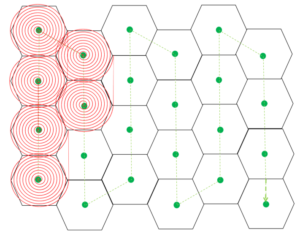
- Spiral scanning to maximise the speed, efficiency and accuracy of the system
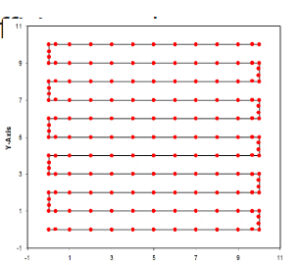 Desirable criteria:
Desirable criteria:
- constant scanning speed
- smooth trajectory with minimal acceleration
- even distribution of laser pulse sites
Tessellating spirals
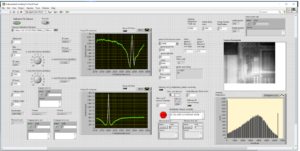
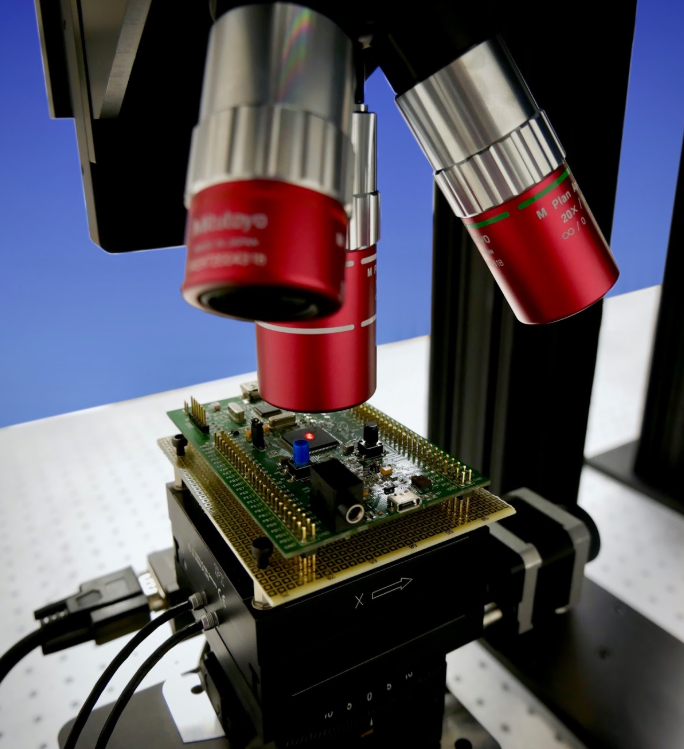
SEE testing examples
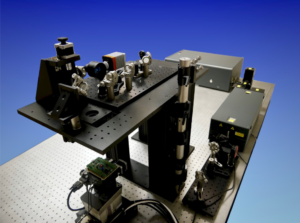
Summary
- Any approach to obtaining radiation performance data on COTS components is better than doing nothing
- The aim is to reduce risk significantly without increasing costs (much)
- Standard SEE testing cannot achieve this but laser SEE testing can
- Using lasers makes SEE testing available and affordable for everyone
- Any approach to obtaining radiation performance data on COTS components is better than doing nothing
- The aim is to reduce risk significantly without increasing costs (much)
- Standard SEE testing cannot achieve this but laser SEE testing can
- Using lasers makes SEE testing available and affordable for everyone
Latest posts by Richard Sharp (see all)


0 comments on The application of laser SEE testing as a new radiation effects validation and screening technique for COTS components