SiC Reliability Testing for Bepi Colombo
- Posted by doEEEt Media Group
- On February 12, 2022
- 0
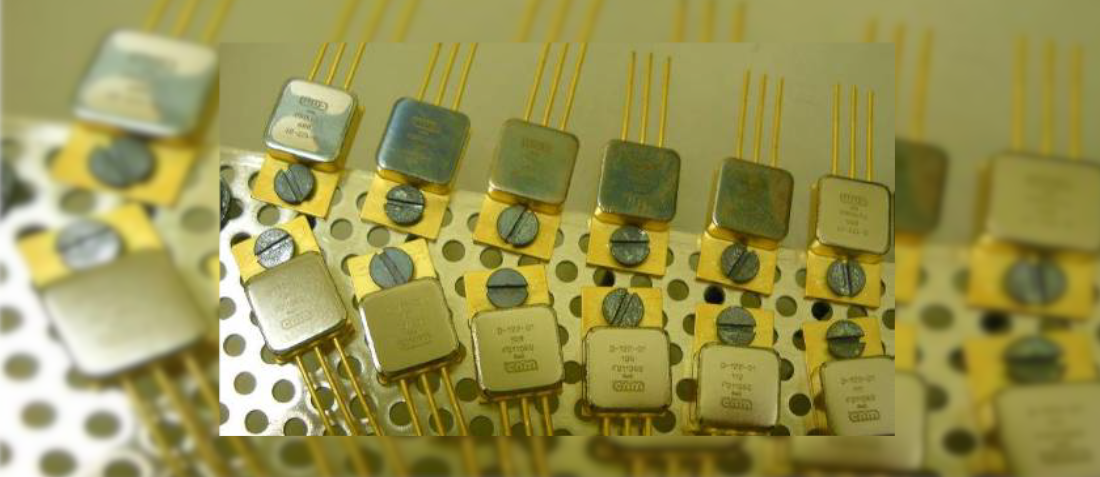
This paper reports the SiC Reliability Testing for Bepi Colombo. The fabrication technology and packaging strategy for 300V-5A SiC Schottky diodes with a wide temperature operation range capability (between -170ºC and 300ºC). These diodes have been designed for harsh environment space applications such as inner Solar System exploration probes. More specifically these diodes are being tested to be the blocking diodes of the solar panels for the Bepi Colombo mission. Different endurance tests have been performed to evaluate the diode behaviour when working at high temperature and under severe thermal cycling conditions (comprised from -170ºC to 285 ºC).
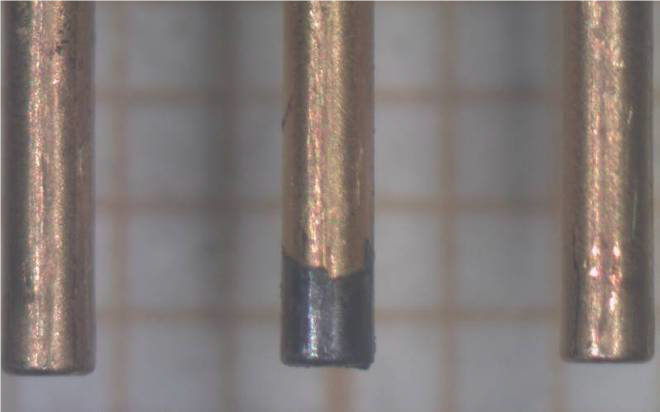
The radiation hardness capability has been also tested. It has been found that the hermeticity of the package is a key aspect to avoid electrical parameters drift. Moreover, the use of gold metallization and gold wire-bonds on the anode allows reducing the diode surface and bonding degradation when compared to Al-containing technology. On the backside cathode contact, the Ti/Ni/Au metallization and AuGe combination has shown a very good behaviour. As a result, the manufactured diodes demonstrated high stability for continuous operation at 285ºC. This SiC reliability testing performed included mechanical test with strong levels of vibration and shocks and constant acceleration, life test at maximum operating conditions with 1500 hours at 285ºC at 5A forward current and 500 hours at 250 reverse voltage and 4000 thermal cycling from -150ºC till 230ºC with forward current of 0.8A for temperature over 25ºC while the voltage drop was being monitored.
The paper includes also a description of the setup solutions and the main lessons learnt for future testing of high power devices operating at a wide temperature range.
The increasing demand for high-temperature electronics has stimulated the research for alternatives to Silicon (Si) capable to operate under extreme working conditions; e.g., in harsh environment, at temperature above 300°C, under high pressures, experiencing intense vibrations or withstanding corrosive liquids. Wide bandgap semiconductors are materials that have attracted much attention, especially due to their superior electrical, mechanical and chemical properties. Currently, the wide band gap material which presents a more mature manufacturing technology is SiC. The recent improvements in SiC material growth, with a strong reduction of defect density in the starting material, allow producing reliable SiC-based devices [1, 2].
This fact has conferred to SiC to be the most adequate candidate for developing high-efficiency converters and high power electronics [3, 4, 5]. The most advanced device from the technical and commercial point of view is the SiC Schottky diode [6,7]. Commercial diodes produced by Infineon or CREE Inc. have shown to be efficient and reliable in standard power applications [8]. Schottky SiC-based devices are an interesting solution for the ever-increasing demand required by space applications, such as BepiColombo mission [9]. BepiColombo mission will consist of two separate spacecraft that will orbit Mercury. Since Mercury is close to the Sun, the expected working temperature of the solar cell and related electronics ranges from -170ºC to +270ºC.
In particular, the MPO (Mercury Planetary Orbiter) will be exposed to Sun intensities up to 10.7 times higher than in Earth’s orbit. The high operating temperature is not the only challenge of this mission. When orbiting around Mercury, the MPO will experience seasonal eclipses. The minimum expected temperature in eclipse is -170°C and the number of cycles is in the range of 4,000. Therefore, this application requires that operating conditions of the blocking diodes must be extended far beyond the limits of existing Hi-Rel diodes.
This work aims to develop SiC Schottky diodes -based devices capable to be used in the BepiColombo mission.
However, the package of the commercially available devices is designed for a maximum junction temperature of 175ºC. Regarding our BepiColombo application, 300V-5A diodes are required with a working temperature capability ranging from -170ºC to 270ºC. The two main challenges to extend the diodes’ state of the art to this particular temperature range were: To define a reliable high temperature package and to modify accordingly the SiC die technology to fit in the novel package. Different technological approaches have been considered, with mainly variations on the interconnection technique and metallization layers. Batches of packaged diodes have been submitted to long term electrical stress to define the optimal design and process flow chart for the diode, focusing on the devices stability in DC mode. Thermal cycling tests have also being performed to evaluate the thermo-mechanical stability.
SiC Schottky Diodes Reliability Testing for Bepi Colombo
Download or read the full report here
Centro Nacional de Microelectrónica (CNM) Instituto de Microelectrónica de Barcelona (IMB), Barcelona (Spain)
GET IN TOUCH TODAY!
Have questions? Contact us
- Space-Grade components available for immediate delivery - April 10, 2025
- Exclusive stock on doEEEt: How to access and request - April 10, 2025
- Managing EEE components for LEO and lower cost space missions - December 17, 2024



0 comments on SiC Reliability Testing for Bepi Colombo