Reliability of Liquid Crystals in Space Photonics
- Posted by doEEEt Media Group
- On February 19, 2020
- 0
Abstract:
Passive liquid crystal (LC) devices are becoming an interesting alternative for the manufacturing of photonic devices in spatial applications. These devices feature a number of advantages in this environment, the lack of movable parts, and of exposed electronics being among the most outstanding ones. Nevertheless, the LC material itself must demonstrate its endurance under the harsh conditions of space missions, including launch and, perhaps, landing. In this paper, we present the environmental testing of an LC device for space applications. A number of LC based beam steering devices were manufactured, characterized, and tested in a series of destructive and nondestructive tests defined by the European Space Agency (ESA). The purpose was to evaluate the behavior and possible degradation of the LC response in simulated space environments.
Introduction
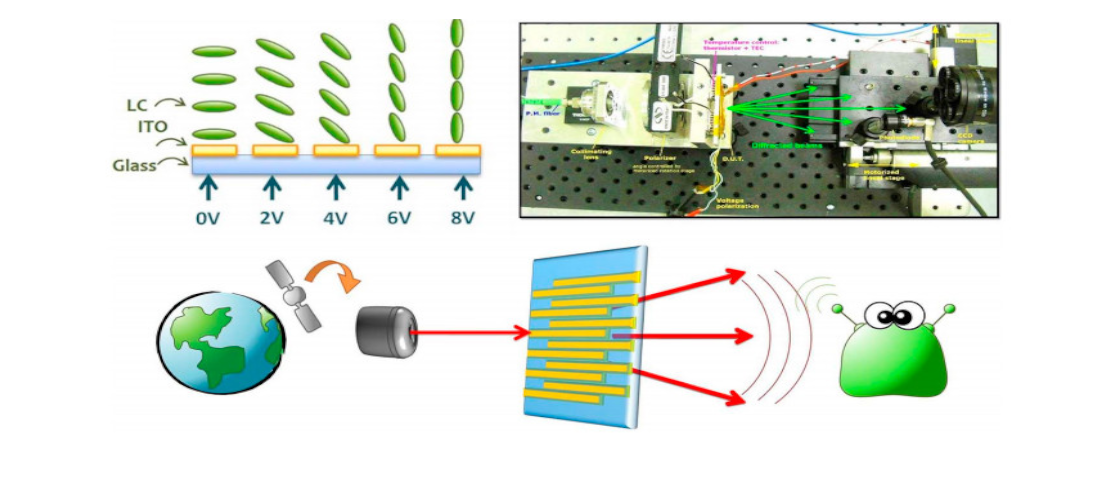
Liquid crystal (LC) devices are increasingly being used in non-display applications to manufacture low-cost, light-weight small devices that can be driven by low-voltage electronics. Avoiding the use of movable parts or mechanical elements is particularly desirable in certain circumstances, e.g., space applications [1]–[4]. Non-display photonic devices based on LCs can be either phase-modulation or amplitude modulation devices [5]. A number of LC photonic devices induces phase delays between different positions of the wavefront resulting in spatial light modulators (SLM) [6], [7]. SLMs have been used in many scenarios, e.g., spatial filters, holograms [8], light-path compensators, tunable lenses [9], or beam steerers [10], [11].
Commercial and experimental LC spatial filters and holograms are chiefly based on active thin-film transistor (TFT) microdisplays or on high-density microdisplays on silicon backplanes aka liquid crystal on silicon (LCoS) displays. Lenses and beam steerers, on the other hand, Vol. 7, No. 4, August 2015 6900909 IEEE Photonics Journal Reliability of LCs in Space Photonics may be manufactured in a number of different styles, including passive-driven and mono pixel solutions. The behaviour of such devices depends on the conducting surfaces, alignment conditions, and LC material; thus, a large number of variables are available for tuning these devices to specific applications [12]–[14].
In this work
We present the results obtained within the context of the ESA-funded project Programmable Optoelectronic Adaptive Element (AO/1-5476/07/NL/EM). The ESA-POE Beam Steering device is a liquid crystal based tunable blazed grating for space applications, i.e., a 1D SLM. A laser beam can be steered certain angles, step-by-step, depending on the grating period. The main goal of the work was to ascertain the suitability of LC photonic devices for spatial photonic devices.
The qualification is done by undertaking several destructive and non-destructive tests defined by ESA. The device manufacturing process was done keeping in mind the conditions and environment the device has to undergo in a space mission: extreme temperature variations, pressure variation, vibrations, and high-energy ionizing radiation. Thus, high-density electronic structures, such as thin-film transistors or LCoS technology, were avoided in the active area. Instead, the pixel addressing is done using passive transparent indium-tin-oxide (ITO) coated onto glass plates, controlled by electronics situated aside the active area. In doing so, only the ITO tracks, the LC, and the supporting substrate will be exposed to external radiation. The remaining electronics can be easily shielded, and system damage induced by radiation becomes largely alleviated.
Read full experimental and result below
Authors: Eva Otón, Javier Pérez, Demetrio López, Xabier Quintana, José M. Otón, and Morten A. Geday CEMDATIC, ETSI Telecomunicación, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Spain
Alter Technology, Spain
- Managing EEE components for LEO and lower cost space missions - December 17, 2024
- Filtering Characteristics of Parallel-Connected Fixed Capacitors in LCC-HVDC - November 21, 2024
- ALTER SPACE TEST CENTER: testing approaches for New Space - September 30, 2024

0 comments on Reliability of Liquid Crystals in Space Photonics