Abstract:
The presentation will address the application of COTS components and modules in modules, equipment or subsystems of different criticality categories for ESA institutional missions.
The work has been performed by a dedicated ESA working group, including a pool of experts in different technological and application domains (material and processes, components, radiation aspects, electrical applications both at subsystem and system level).
The approach intends to keep a balanced approach especially between reliability and radiation performances, according to a progressive scheme from higher to less risk taking, and allowing both an economic/experimental (but more risky) use of COTS for cost reduction reasons, and a reliable (but expensive) use of COTS for performance reasons.
Since typically not large, but small procurement lots of COTS components and modules apply to ESA missions, a special care has been given to address expected or not sure lot homogeneity (not only for reliability aspects, but also in terms of radiation tolerance).
In fact, only with guaranteed lot homogeneity one can be sure that the flight specimen has the same properties of the part that is evaluated, “qualified” and/or screened on ground.
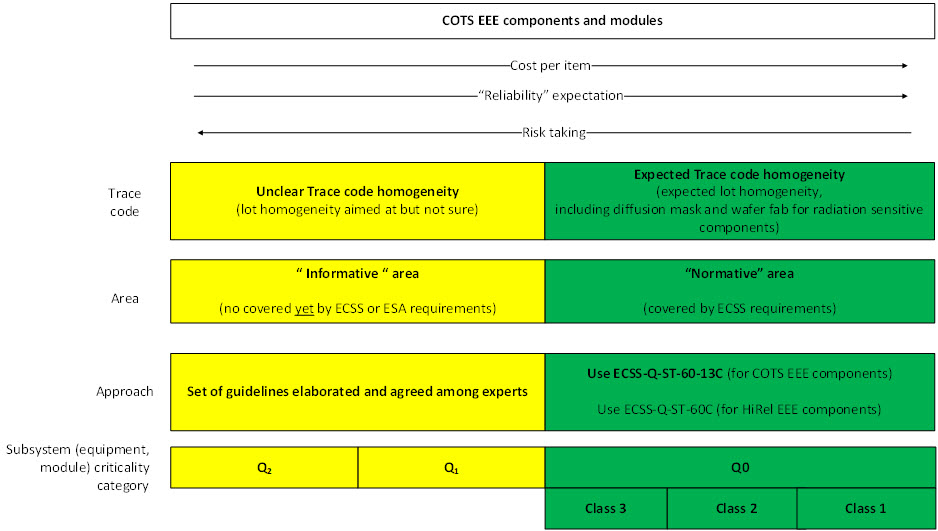
Considering that the approach provides a set of guidelines and not requirements, the identified criticality categories at modules, equipment or subsystem level are divided in two main groups: a normative (“green”) area and an informative (“yellow”) one.
See Figure 1.