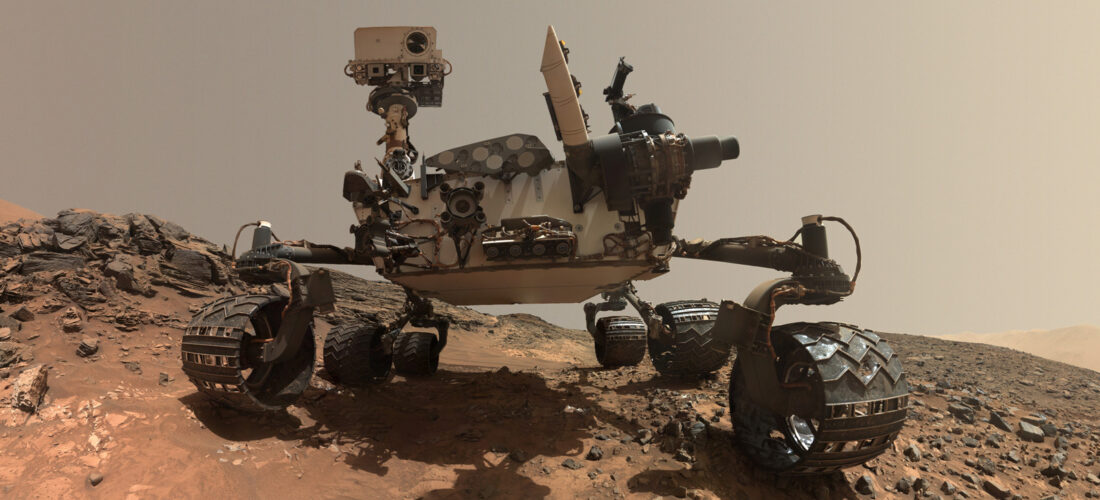

Mars Curiosity Rover: Characterization of photodiodes at cryogenic temperatures
- Posted by Juan Barbero
- On February 14, 2022
- 0
The methodology used for the characterization of the ultraviolet photodiodes used in the Mars Curiosity rover.
The study of the Mars atmospheric conditions is of great importance for both, the preparation of future missions as well as the verification of the actual atmospheric situation during the operation of instruments on Mars. ALTER has actively participated in the REMS (Rover Environmental Monitoring Station) and MEDA (Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer) projects for the development of environmental stations working on Curiosity and Perseverance rovers respectively.
- REMS- The Rover Environmental Monitoring Station is nicknamed REMS, and it contains all the weather instruments needed to provide daily and seasonal reports on meteorological conditions around the rover.
- MEDA- The Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer is known as MEDA. It makes weather measurements including wind speed and direction, temperature, and humidity, and also measures the amount and size of dust particles in the Martian atmosphere.
This success case describes the methodology used for the characterization of the ultraviolet photodiodes used in the Curiosity rover. These photodiodes are placed on the external side of the rover looking to the top for the characterization of the UV radiation at the surface of Mars and, therefore, are exposed to Mars challenging atmospheric conditions.
Introduction
The Mars Science Laboratory mission’s Curiosity rover, the most technologically advanced rover ever built, landed in Mars’ Gale Crater the evening of August 5, 2012, using a series of complicated landing maneuvers never before attempted. Curiosity’s mission is to determine whether the Red Planet ever was, or is, habitable to microbial life. The rover, about the size of a small car, is equipped with 17 cameras and a robotic arm containing a suite of specialized laboratory-like tools and instruments. One of these instruments is the REMS (Rover Environmental Monitoring Station), developed by CAB-INTA (Centro de AstroBiologia) and CRISA with the support of several other companies. ALTER TECHNOLOGY was responsible, among many other tasks, for the calibration of the response of the UV (Ultra Violet) photodiodes used to monitor the low wavelength radiation that arrives at the surface of Mars. The study of this radiation is of paramount importance for future missions to Mars.
The main aim of the UV-Sensor is to characterize the UV environment at the surface of Mars, using detectors that measure the incoming UV radiation.
This sensor was accommodated on the rover deck near the base of the mast. The sensor is essentially a set of UV photodiodes mounted on a specific mounting. Six silicon carbide photodiodes were the selected option to compose the sensor. They were used as photovoltaic photodiodes with 1mm2 dice. Each photodiode had a filter in a different UV range. These are the six other UV channels required for scientific goals:
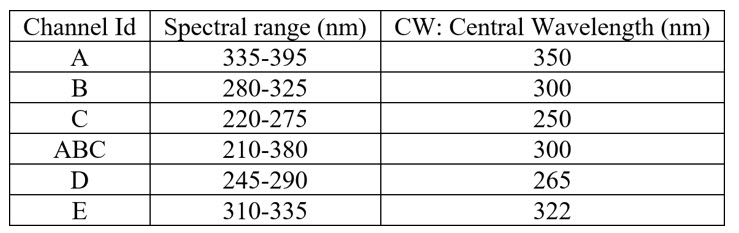
The Field Of View (FOV) is ± 30 degrees and the calibration of the response of each photodiode with the angle was also required.
The photodiodes are surrounded by magnets as in the following figure as a dust magnetic filter to deviate dust deposition. The six photodiodes with their correspondent filters and magnets are inserted in an aluminium box.
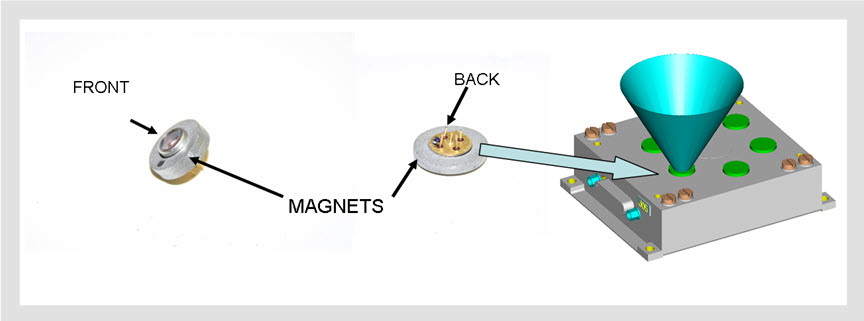
Figure: Left, photodiodes with magnets, Right, UV Sensor Housing
The following picture shows the Curiosity rover on Mars and the location of both the REMS station and the UV photodiodes.

Mars Curiosity Rover: Test setups and results
Characterization of the UV photodiodes within the Mars temperature range
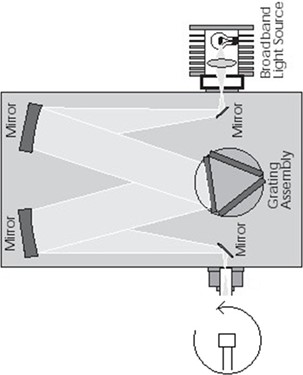
The calibration of the spectral response of the UV photodiodes in the Mars ambient temperature (from -135ºC to +105ºC) was a challenge as the photodiodes had to be characterized in the entire required temperature range. At the same time, all the testing instruments should be in laboratory conditions. The setup was based on using multimode, an optical fiber bundle to guide the light of the source, and the monochromator to both the UV photodiode under test and the reference optical power meter. The following scheme shows the proposed setup:
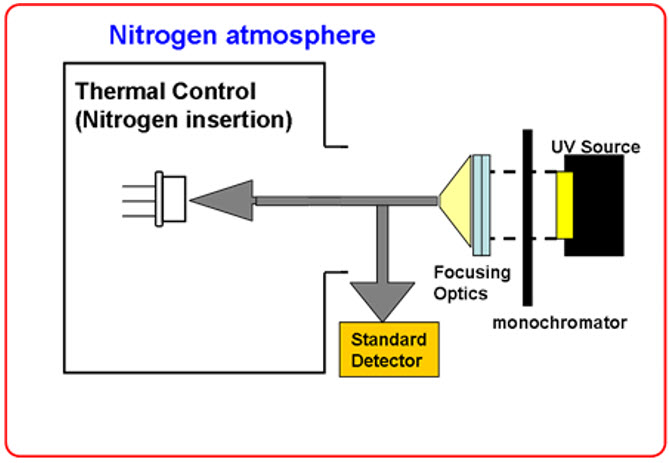
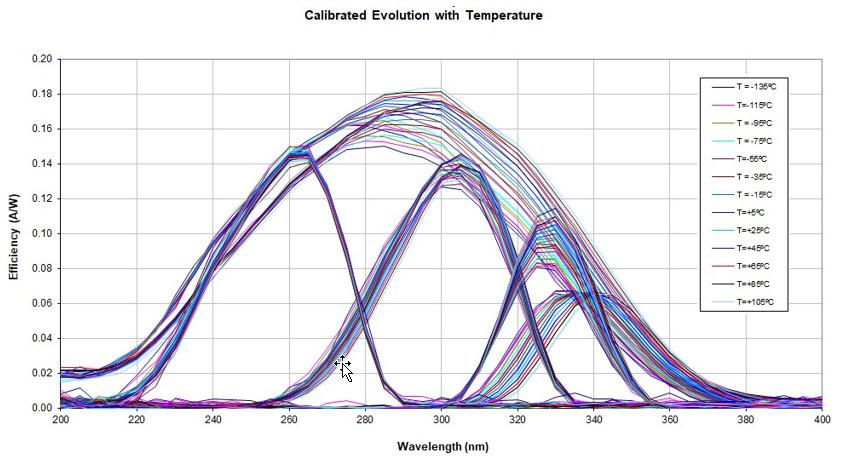
The following picture shows the spectral response evolution measured by ALTER TECHNOLOGY within the required temperature range for all the photodiodes with each type of filters.
Characterization of the UV photodiodes with the illumination angle
The setup used for the angle response calibration was based on placing the photodiodes at 3cm of the output of the monochromator. This output is a window of a diameter of 1 cm approximately. The components were rotated as indicated in the following picture (azimut axis) and around their (polar axis) axis.
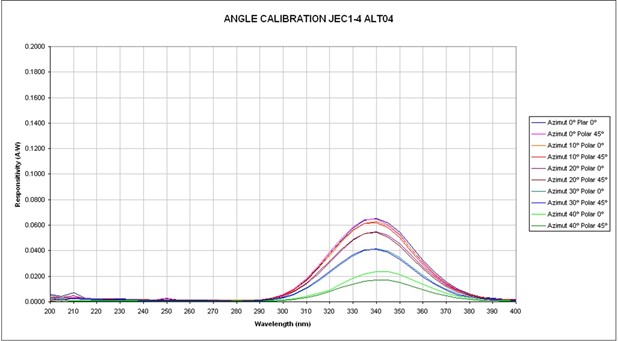
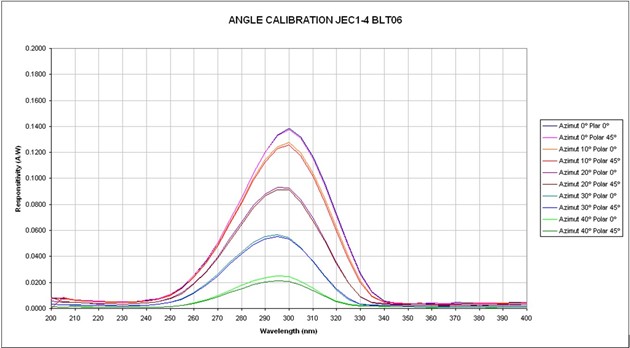
The following pictures show the response with angle obtained for two of the filters as an example. The photodiodes with all the filters were calibrated. These pictures are given as an example.
Mars Curiosity Rover: Conclusion
The calibration of the response of the UV photodiodes sent to Mars with the Curiosity rover within the operating temperature and with incident angle was done by ALTER TECHNOLOGY. These photodiodes have been characterizing the ultraviolet light arriving at the surface of Mars for several years. The information obtained will be very useful for future missions to Mars.
GET IN TOUCH TODAY!
Have questions? Contact us
About Curiosity Rover Mission
Part of NASA’s Mars Science Laboratory mission, within NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, Curiosity is the largest and most capable rover ever sent to Mars. It launched Nov. 26, 2011, and landed on Mars at 10:32 p.m. PDT on Aug. 5, 2012 (1:32 a.m. EDT on Aug. 6, 2012).
Curiosity set out to answer the question: Did Mars ever have the right environmental conditions to support small life forms called microbes? Early in its mission, Curiosity’s scientific tools found chemical and mineral evidence of past habitable environments on Mars. It continues to explore the rock record from a time when Mars could have been home to microbial life.
- CHARACTERIZATION OF STRAIN GAGES - February 16, 2022
- JUICE – JUpiter ICy Moons Explorer - February 14, 2022
- Mars Curiosity Rover: Characterization of photodiodes at cryogenic temperatures - February 14, 2022


0 comments on Mars Curiosity Rover: Characterization of photodiodes at cryogenic temperatures