Hot Solder Dip Acceptance Criteria
- Posted by Antonio Rodríguez Arenas
- On December 20, 2019
- 0
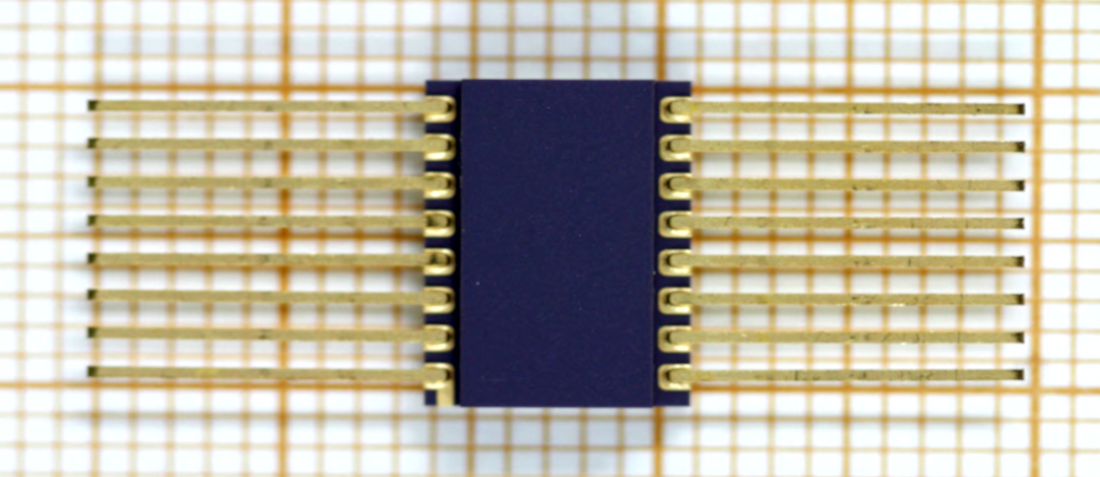
Difference among ESA and MIL Flat Package Hot Solder Dip criteria
Typical leads finish for an integrated circuit with Flat Package for MIL and space applications are gold finish and hot solder dip. Hot solder dip parts produced from an edge, termination or material which was initially gold-plated, the gold removed, and the final solder finish applied.
Per ESCC criteria, ECSS‐Q‐ST‐70‐08C paragraph 7.2.4, the solder must not reach the package and there is a minimum distance of 0.75mm but in contrary MIL specification and DLA accept that the solder is nearer to the package for Flat Packages and the solder cover the pads which are over the package. Therefore, there is a discrepancy among ESCC and MIL.
MIL-PRF-38535L paragraph A.3.5.6.3.4:
For top brazed and bottom brazed flat-pack packages, the hot solder dip shall be within 0.070 inches (1.78 mm) to the lead/package interface. For all brazed flat-pack packages, the solder finish may be on the brazed pad interface area.
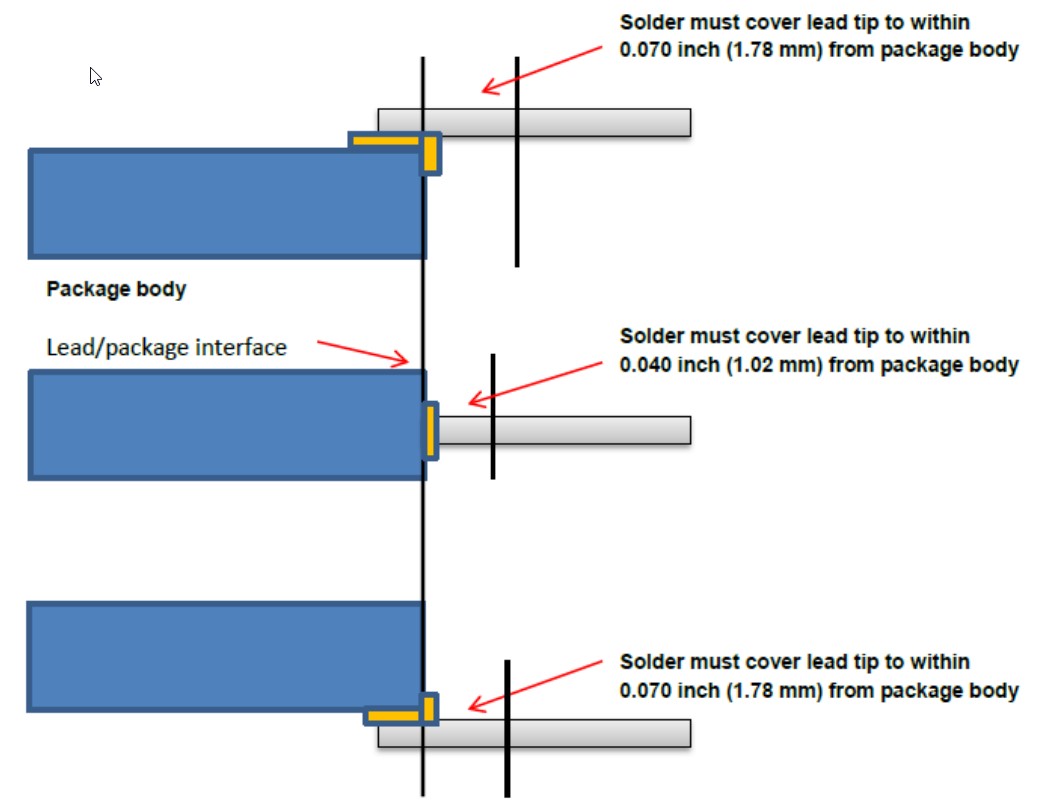
MIL-PRF-38535L paragraph A.3.5.6.3.4 Figure A-1. Solder dipping area when seating plane is not defined
The users of these parts that use in general ESCC criteria tends to identify these findings as rejects, but in the cases that they procured with to MIL-PRF-38535, hey are acceptable. No NCRs are needed to trace these findings since the parts are compliant with procurement specification.
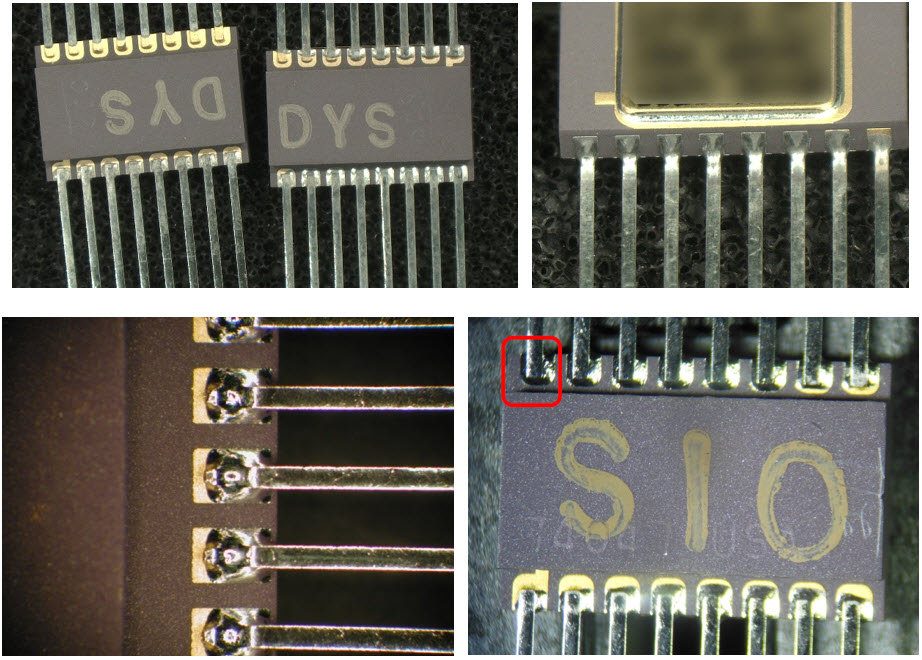
The following pictures show examples of acceptable parts according to MIL-PRF-38535L paragraph A.3.5.6.3.4.
Contact us for more information
- Quality Issues in the procurement of Operational Amplifiers - April 20, 2021
- MICROCHIP FPGAs External Visual Inspection Considerations - January 20, 2020
- RGA (Residual Gas Analysis) STATISTICS - January 2, 2020

0 comments on Hot Solder Dip Acceptance Criteria