Commercial components vs lead-free terminations; how to manage it?
- Posted by Cédric Clement
- On December 3, 2019
- 0
The use of commercial parts is not a new topic
- Airbus Defence & Space participate to various working groups establishing adequate part policy for using active commercial parts for space applications.
-
-
- ECSS-Q-ST-60-13 standard (Space Product Assurance, Commercial electrical, electronic and electromechanical (EEE) components).
-
-
- Based on this standard, it is possible to select, procure and use several components not available in HIREL quality level .
-
-
-
- Active parts with higher integration, higher performances.
-
-
- SnPb terminations for commercial (including automotive) parts not available.
-
-
- According to the standard , retinning of parts with pure tin terminations is required.
- For ADS, retinning is seen as bringing more risk (additional handling of components & thermal constraints are not well controlled).
-
-
Trends/Market/REACH
- Space components market represents less than 0,1 % of the Global market
HIREL parts (SnPb finish) represent less than 0,1 % of Lead-Free finishes
- European Legislation has focused electronics industry attention on the interdiction of lead in electronics assembly : REACH
-
-
-
- Anticipation of the future lead free regulation
- 2019 ESA/ESCC Working group on lead-free transition (in progress)
-
-
LEAD-FREE finish on commercial parts
- Lead-free components does not mean “pure tin” components (e.g. SnAgCu, NiPdAu,…)
- Example : equipment on Constellations programs (not experimental missions) requiring a high degree of quality/reliability.
-
- Alternatives in term of management, selection, procurement and usage of components (components not available in HIREL quality level and reduce the cost of ownership of components).
-
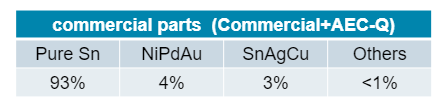
Most parts are Pure Tin
Commercial parts are designed for Lead-free process
Compatibility with current SnPb mounting process?
LEAD-FREE Transition schedule
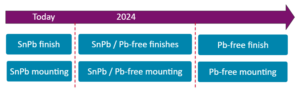
Finishes of components VS mounting process
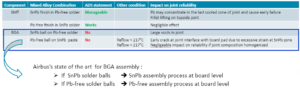
In case of incompatibility, the material must be “respected”
Points of attention during commercial parts selection
- TSSOP/SOIC package are preferred options compared to QFN.
- Lead-frame material : copper alloy is preferred as closer to PCB dilatation
-
- Packages with Iron nickel Lead-frame could affect the mounting reliability
-
- Molding compound type varies with package and manufacturer (different Tg et CTE)
-
- Qualification of package and/or manufacturer by similarity is less obvious with commercial parts than HIREL parts
- PCN affecting molding (new molding, new assembly site) or bonding (gold wire -> copper wire) : requalification of package.
-
- Manufacturer lead finish transition : HIREL SnPb part switched in lead-free variante.
-
-
-
- Parts to be selected with precaution because HIREL manufacturers processes are not (yet) mature.
-
-
-
Lead finish synthesis
-
-
- The lead finish is obviously the main change for lead-free process.
-

-
-
- For others finishes, compatibility of soldering process has to be checked “case by case”
-
PURE TIN MANAGEMENT
- Current space standard do not recommend the use of Pure Tin (Tin Whiskers).
- ADS strategy and material restriction
-
- Parts with bright pure tin plating (>97% tin) on terminations shall not be used.
- Parts with mate pure tin finish (>97% tin) are allowed, provided they pass the JESD-201 class 2 requirements or meet the GEIA-STD-0005-2/Class 2B requirements.
- Parts with pure tin finish not to be used in power functions (V > 15V and I > 2A) or screwed on board.
- When JESD-201 class 2 is not demonstrated, the use of conformal coating is considered as an acceptable risk mitigation.
-
-
- Most of manufacturers mitigate at component level, (1hours baking @ 150°C after tin deposit, thickness of the under-layer (Ni), or Low percentage other metals to reduce whiskers growth (and others).
Pure Tin finish is manageable
Airbus Group status on lead free assembly reliability
 Many studies conducted within Airbus Group on lead free assembly reliability
Many studies conducted within Airbus Group on lead free assembly reliability- For Space activities, CNES study conducted in 2016-2017.
-
- Several types of SMT packages with different finishes, assembled on lead free assembly line.
-
-
-
- Tested through vibration & thermal cycles [-55°C ; 100°C], until 2000 cycles.
-
– Results presented during COMET event, May 16 2019 –
- Main outcomes : As soon as the assembly process is well defined.
-
- Reliable assemblies with tin lead process remain reliable with lead free process
- Critical assemblies (ex : TSOP with iron nickel leads) remain critical with-lead free process
- No difference was identified compare to different component finishes (similar solder joint reliability)
- In general, failure mode remains the same with lead-free process
- BGA not evaluated in the frame of this study
-
These statements were confirmed by other French industrials during COMET workshop
SYNTHESIS
- Most of the commercial parts have pure tin finish
-
- Whiskers need mitigation, but most of the commercial manufacturers know how to manage it.
-
- Commercial parts are designed and validated for lead-free mounting process.
-
- Attention have to be brought to the package selection (lead-frame material, package type…).
- Validation step is necessary (take care of the package similarity).
-
- The compatibility with the SnPb mounting process is generally good (similar to Pb free solder process), except BGA with SAC balls, not recommended to be SnPb soldered.
- The main encountered difficulties are not with commercial parts , but with specific components or adapted from HIREL.
Most of the lead-free commercial parts problematics are manageable
- Commercial components vs lead-free terminations; how to manage it? - December 3, 2019

0 comments on Commercial components vs lead-free terminations; how to manage it?